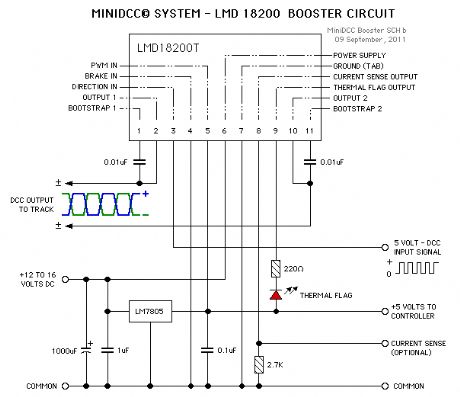
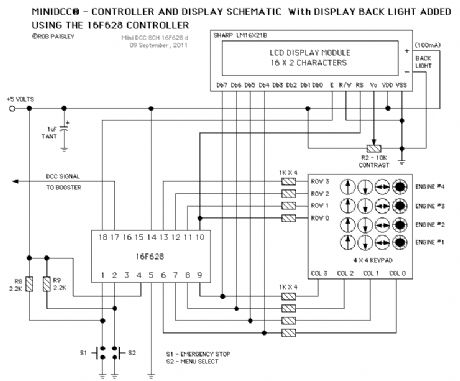
Circuit Diagram
Index 91
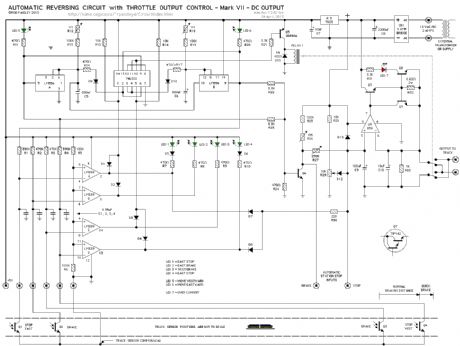
Automatic Reversing Circuit Schematic - DC Output
Published:2013/6/21 3:04:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: Automatic Reversing Circuit, DC Output
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(669)
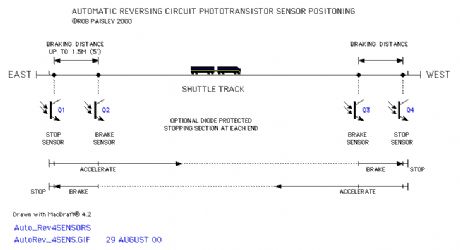
phototransistor sensors
Published:2013/6/21 3:04:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: phototransistor sensors
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(580)
Flip-Flop circuit
Published:2013/6/21 3:02:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: Flip-Flop circuit
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(729)
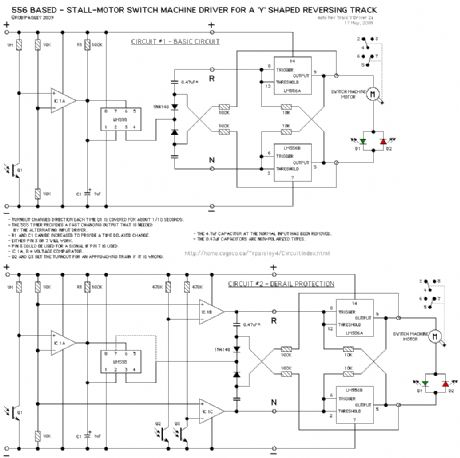
'Y' TRACK SWITCH MACHINE CONTROL
Published:2013/6/21 3:02:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: 'Y' TRACK SWITCH, MACHINE CONTROL
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
OUT-AND-RETURN OPERATION
Published:2013/6/21 3:01:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: OUT-AND-RETURN OPERATION
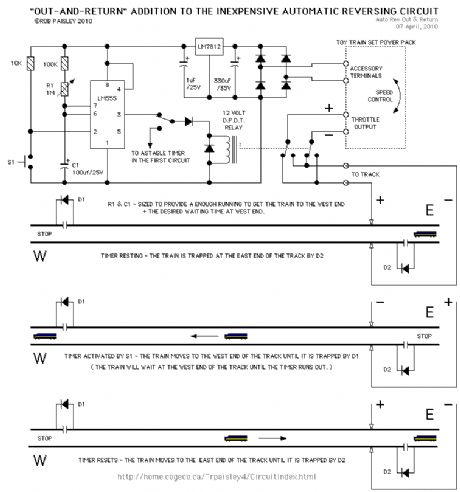
In this circuit the train only moves when S1 is pushed. After a set waiting time the train returns to its start position and then waits.
The 555 timer in this circuit is configured as a monostable oscillator. The SPDT switch allows the circuit to be changed from normal operation to out-and-back operation. Two 555 timers are indicated but a 556 timer can also be used. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(601)
STATION STOP
Published:2013/6/21 3:01:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: STATION STOP
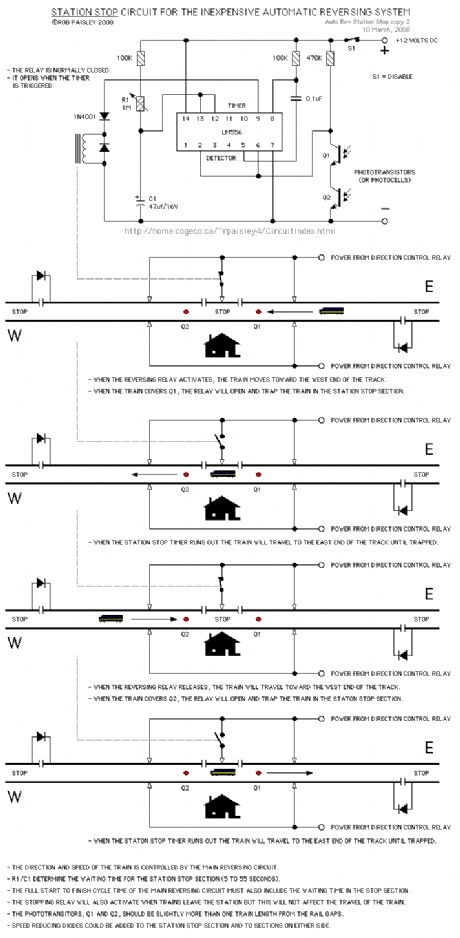
This circuit will stop and start the train at a station located on the reversing track.
This circuit is as simple as possible, using the bottom section of a 556 timer as a photodetector and the top section as the delay timer.
The timing circuit takes its control and track power from the power supply circuit on this page.
NOTE: When using this circuit, there are other things to consider, such as; train length and whether the locomotive has all wheel pickup. These can affect the placement of the gaps and phototransistors. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1000)
PSEUDO SPEED CONTROL
Published:2013/6/21 3:00:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: PSEUDO SPEED CONTROL
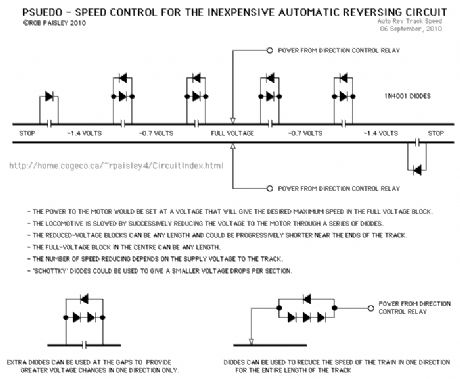
This track circuit uses diodes and gaps to provide a crude form of speed control. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(761)
longer stopping sections
Published:2013/6/21 2:59:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: longer stopping sections
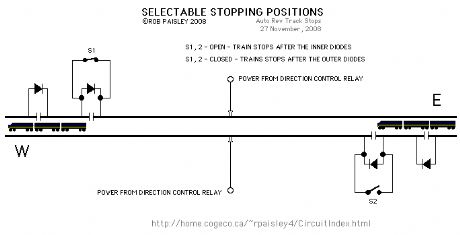
The next diagram shows how to provide increased stopping distances for trains with head-end power. The longer stopping sections can be switched if the train is reversed. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(700)
BASIC TRACK CIRCUIT
Published:2013/6/21 2:59:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: BASIC TRACK CIRCUIT
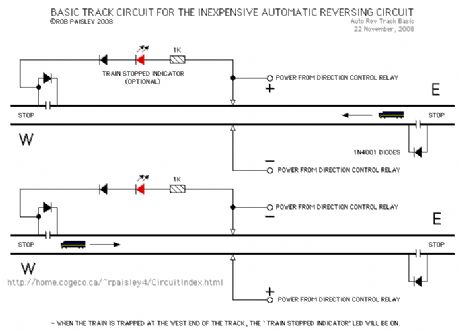
The basic track circuit provides continuous back and forth operation of the train with diodes and gaps to stop the train at each end of the track.Also shown is an optional LED that will show when the train has been trapped at the end of the track. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(957)
POWER SUPPLY and TIMER
Published:2013/6/21 2:58:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: POWER SUPPLY and TIMER
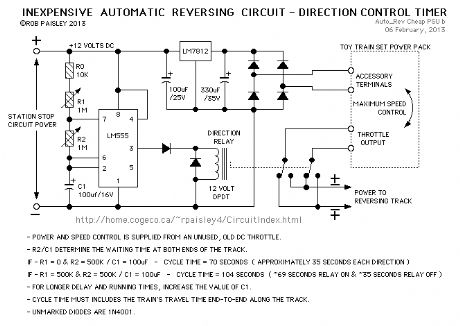
The power supply circuit provides power to the track and has a 12 volt power source for the 555 timer IC that controls the waiting time at each end of the track.
NOTE: The circuit does not know when or how fast the train is moving, therefore the timer's cycle times must also include the time for the train to travel along the track in either direction. For example it the train is to wait for 30 seconds at the end of the track, the timer will be set for: The time to travel to the end of the track + 30 seconds.The reversing switch on the power pack itself is only used to set the initial travel direction of the system or to 'switch ends' if the waiting times are not equal.
The calculator at the following link can be used to determine values for resistors R1 and R2 and capacitor C1. (LM555 - Astable Oscillator Calculator)
(View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(698)
Alternate Location Control
Published:2013/6/21 2:53:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: Alternate Location Control
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(824)
CURRENT LIMITING RESISTOR CALCULATOR FOR LIGHT EMITTING DIODES
Published:2013/6/21 2:52:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: CURRENT LIMITING RESISTOR CALCULATOR , LIGHT EMITTING DIODES
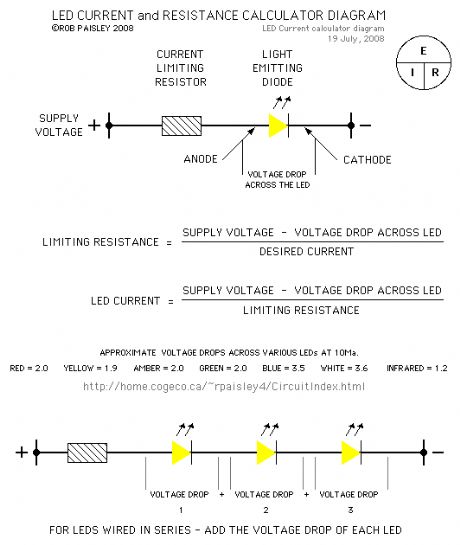
The calculators on this page can be used to find current limiting resistors and currents for Light Emitting Diodes.
The first calculator determines the resistance for a desired LED current while the second calculates the current for a given resistance. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(806)
Block Occupancy Detector Helper Circuit
Published:2013/6/21 2:52:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: Block Occupancy Detector, Helper Circuit
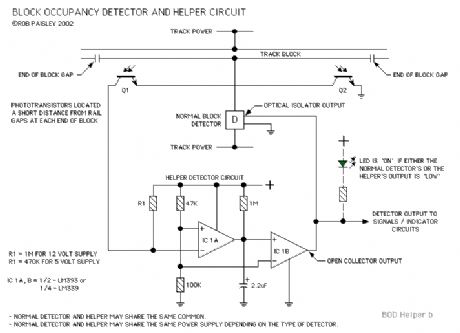
This circuit would be used to hold a BLOCK OCCUPIED condition as a train passes out of the block even if the normal detector is not sensing a train.
The Helper circuit uses phototransistor type light activated detectors to sense that a train is still in the block, even though the engine has left that block.
The only reason to use this circuit is if there are no conducting wheel sets at the tail end of the train that would keep the normal occupancy detector activated until the train has completely exited from the block.
Simply stated the Helper circuit's output is in parallel with that of the normal detector. When the Helper circuit is activated by a train covering one of the phototransistors at either end of the block, the Helper's output holds the block as occupied even though there is no current flowing through the sensing circuit of the normal detector and has therefore turned OFF. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(771)
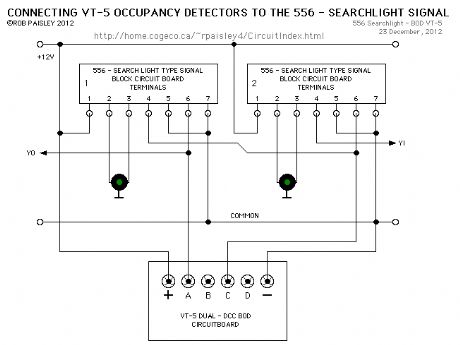
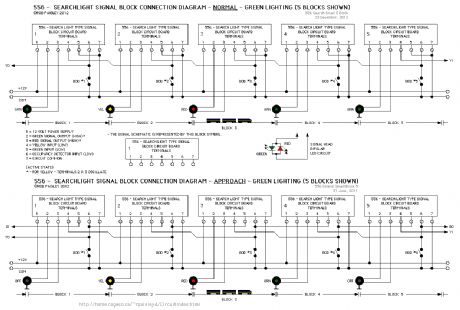
556 - Searchlight Signal Driver
Published:2013/6/21 2:51:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: 556 , Searchlight Signal , Driver
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(713)
Multiple Block Signal Connections
Published:2013/6/21 2:50:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: Multiple Block Signal Connections
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(935)
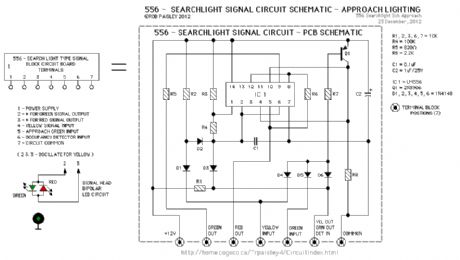
556 - Searchlight Signal Driver Schematic
Published:2013/6/21 2:50:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: 556, Searchlight Signal , Driver Schematic
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1054)
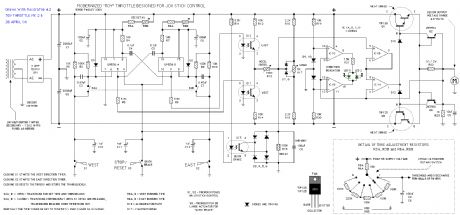
Joy Stick Controlled - Modernized "Toy" Throttle Mk.2 Circuit
Published:2013/6/21 2:49:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: Joy Stick Controlled , Modernized "Toy", Throttle, Mk.2 Circuit
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(713)
3Amp - DCC Booster Circuit #1
Published:2013/6/21 2:48:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: 3Amp , DCC Booster Circuit
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(643)
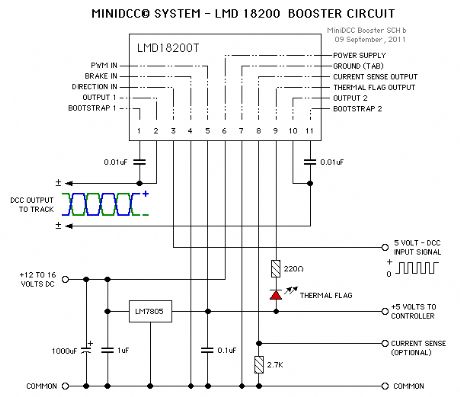
MiniDCC© H-Bridge Circuit
Published:2013/6/21 2:47:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: MiniDCC© H-Bridge Circuit
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(474)
MiniDCC© Circuit Board Connection Diagram
Published:2013/6/21 2:47:00 Author:muriel | Keyword: MiniDCC©, Circuit Board, Connection Diagram
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(895)
| Pages:91/2234 At 2081828384858687888990919293949596979899100Under 20 |
Circuit Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit