
Index 164
2_METER_SCANNER
Published:2009/7/13 23:35:00 Author:May
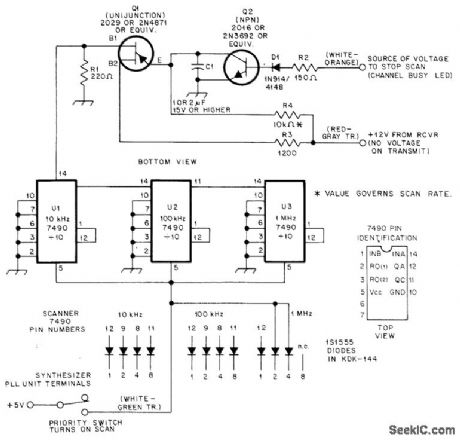
Designed for use with KDK-144 amateur 2-meter transceiver to provide automatic scanning between 146 and 147.990 MHz. When transceiver is switched to priority position, +5 VDC is applied to 7490 decade counters U1, U2, and U3 to activate scanner. Scanning stops when signal strong enough to open squelch turns on Darlington-connected transistors a1 and Q2, shorting UJT timing capacitor C1 which is 1-2 μF.-R. W. Shoemaker, Jr., A Scanner for KDK, QST, 0ct. 1978, p 36-37. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(869)
DECADE_SCALER
Published:2009/7/13 23:34:00 Author:May
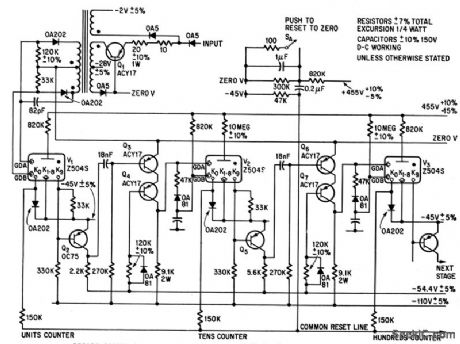
For accurate timing applications up to 400 pps.-G. Jeynes, Using Cold.-Cathode Tubes to Count and Store, Electronics. 38:8, p 80-89. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(540)
HIGH_SPEED_FLIP_FLOP
Published:2009/7/16 1:39:00 Author:Jessie
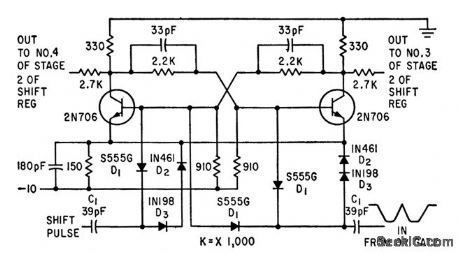
Used in producing complex pulse sequences up to 4 billion bits in length. Drives n-stage shift generator that provides modulo-2 additions.-B. K. Ericksen and J. D Schmidt, Random Pulse Generator Tests Circuits, Encodes Messages, Electronics, 34:25, p 56-59. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(560)
CRICKET_CHIRP_SIMULATOR
Published:2009/7/13 23:32:00 Author:May

Power is supplied from a 9-V battery, B1; current drain is a little under 2 mA, so an alkaline battery should last more than 250 hours. Switch S1, the power switch, is a part of potentiometer R10, which also acts as a volume control. A duty cycle is generated by op amp U1-a, which is configured as a pulse generator. Diode D1 establishes a fast charging rate that generates a 0.22-second period, which matches the duration of a cricket's seven-beat chirp. The discharge rate is established by R2 to generate a reset time of 0.35 second. One half of an ICM7556 CMOS timer, U2-a, is used to simulate the amplitude modulation of a chirp. Timer U2-b is configured as a conventional pulse generator with a symmetrical duty cycle and an output frequency of 2 kHz. The output of U2-b is used to switch Q2 on and off, which produces a voltage across volume control R10 that has the magnitude of the instantaneous voltage across C2 with a 2-kHz sampling rate. A portion of that voltage is applied to U1-b, which is configured as a unity-gain, noninverting buffer that drives the piezo element. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(827)
REMOTE_TUNING
Published:2009/7/13 23:32:00 Author:May
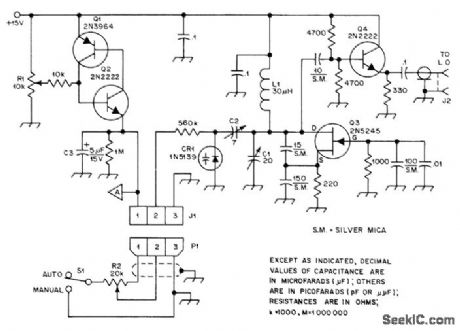
Simple sweep generator and 5-5.5 MHz VCO provide remote manual or automatic electronic tuning of 6-meter transceiver, for quick check of possible band openings a few kilohertz from frequency to which receiver is normally tuned. To adjust, set S1 on MANUAL and turn R2 fully counterclockwise. If signal at lowest received frequency is applied to antenna jack, signal can be centered within IF passband of receiver by adjusting C1. Next, turn R2 fully clockwise, apply signal at highest frequency to be received, and center signal within passband again by adjusting C2. With S1 in AUTO position, R1 determines highest frequency tuned. If sweep rate is too low, reduce value of C3. Point A is used to drive CRO through FET buffer stage, for displaying signals present within sweep range as pips on screen.-J. R. Bingham, Sweep 6 Meters and Really Clean Up! QST, April 1977, p 27-28. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1438)
COUNT_STORAGE
Published:2009/7/13 23:27:00 Author:May
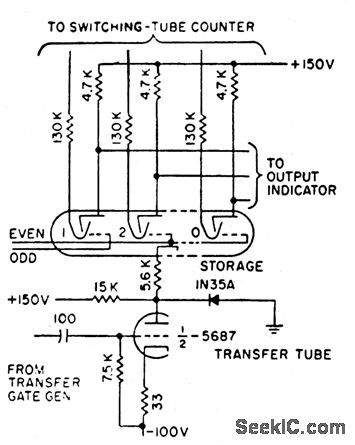

Magnetron beam-switching tube and transfer tube together serve to sample and store accumulated count and provide multioutput functions without stop-ping original count or losing input information during readout.-R. W. Wolfe, Decode Decimal Counter Speeds Printed Readout, Electronics, 31:3, p 88-90. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(519)
ELECTRONIC_NOISEMAKER
Published:2009/7/13 23:25:00 Author:May
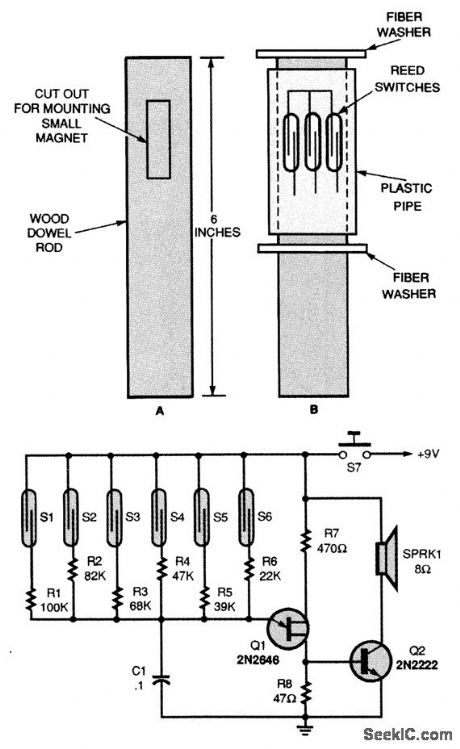
A single unijunction transistor, Q1, generates the different tones, and a general-purpose NPN transistor, Q2, raises the level to drive a small speaker. The six reed switches, S1 to S6, are mounted around the outside of the plastic pipe (Fig. B). As the pipe turns over the magnet, the reed switches open and close, tying different-valued resistors to the oscillator's frequency-control circuitry. It is also possible for two reed switches to be closed at the same time. When that happens, the output tone will be much higher in frequency than when only one switch is activated. The oscillator's frequency range can be lowered by increasing the value of C1, and raised by decreasing C1. To operate, just grab the noisemaker by the dowel rod and give it a twist to start the plastic case turning. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(713)
SCANNER
Published:2009/7/13 23:24:00 Author:May

Provides eight combinations of four transmit and four receive frequencies under digital control using same four wires going to control head originally in four-channel commercial FM mobile transceiver. Also pro-vides scanning of up to eight receive channels. Uses SN7442 BCD-to-decimal decoder. Switch in original control head is rewired to count in BCD format. Carrier-operated circuit stops clock when signal is received during scanning, and readout device displays number of channel being received. Clock is UJT 02 with 500K pot varying scanning rate. Article covers construction and testing.-C. Durst, Scanning Adapter for FM Transceivers, 73 Magazine, April 1973,p73-78.
(View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(991)
ELECTRONIC_TROMBONE
Published:2009/7/13 23:23:00 Author:May
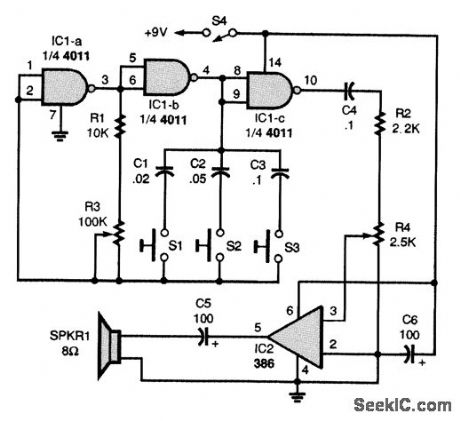
The heart of the trombone is R3, a slide potentiometer. Two gates of a quad two-input NAND gate, IC1-a and IC1-b, make up a simple audio-oscillator circuit, with R1, R3, C1, C2, and C3 setting the oscillator's frequency:The oscillator's output is buffered by IC1-c, which also supplies the drive signal for the power amplifier, IC2. The trombone's output level is set by R4. A slide handle, made of plastic or wood, should be attached to the slider of R3. The complete circuit, enclosed in a small plastic cabinet, with the three push-button switches, S1 to S3, mounted in a convenient location for playing. Just press one or more of the tone-control switches, S1 to S3, and work the slide. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(937)
COUNTING_UP_TO_100_KC
Published:2009/7/13 23:21:00 Author:May
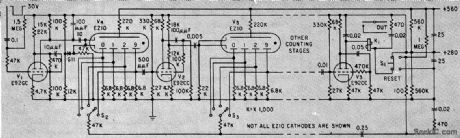
Uses miniature gas-filled decade counters that provide visual indication of count along with high reliability. Schmitt-trigger input feeds mono between counter tubes. Can produce output after desired count if counter is initially reset to complement of the desired number.-K. Apel and P. Berweger, Miniature Gas-Filled Tubes For High-Speed Counting. Electronics. 33:8,p46-47. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(633)
STANDARD_MICROMODULE_LOGIC_GATE
Published:2009/7/16 1:38:00 Author:Jessie
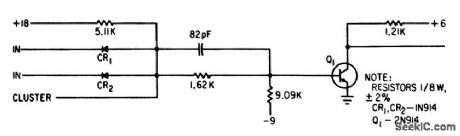
Single-transistor gate can have maximum fan-in of 20 and maximum fan-out of 4. Power dissipation is 75 mw average, pair delay is 60 nsec, and rise time 30 nsec.-A. S. Rettig, Computers in the Front Lines: Micromodules Make if Possible, Electronics, 36:1, p 77-81. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(505)
THREE_STAGE_ENCODER
Published:2009/7/16 1:38:00 Author:Jessie
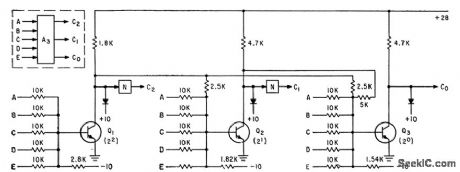
With 2N1499 transistors, settling time of encoder for simultaneous multiplier is less than 0.4 microsec, and maximum time to produce 8-bit product is about 1.2 microsec.-S. C. Chao, High Speed Encoding with Resistor-Transistor-Logic Circuits, Electronics, 35:6, p 48-51. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(690)
TRANSISTOR_SERIES_SWITCH
Published:2009/7/16 1:37:00 Author:Jessie
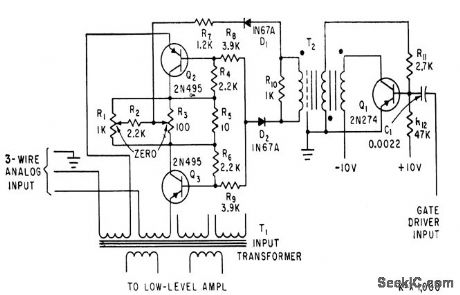
Two transistors back-lo-back in inverted connection serve as and gate between analog input from instrumentation transducer and input transformer of multiplexer. Gate driver receives key pulse from timing matrix.-C. E. Griffin, J. P. Knight, and J. H. Searcy, Low. Level Multiplexing for Digital Instrumentation, Electronics, 33:41, p 64-66. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(719)
TICK_TACK_TOE_LOGIC
Published:2009/7/16 1:37:00 Author:Jessie

Neon lamps serve as diode gates and indicate positions and moves on game board. Thyratron-relay com bination serves as memory, while relays referee sequence to prevent two successive moves by either player.-C. E. Hendrix and R. B. Purcell, Neon Lamp Logic Gates Play Tick-Tack-Toe, Electronics, 31:25, p 68-69. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1688)
PULSE_SECIUENCE_DETECTOR
Published:2009/7/16 1:36:00 Author:Jessie
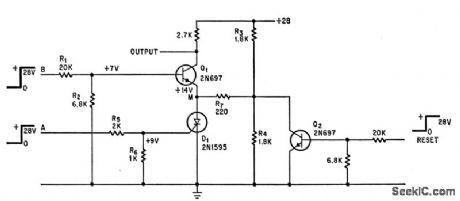
Output occurs only when event signal at A precedes event signal at B. Other sequences are ignored.-R. A. Wilson, Two Events, in Sequence, Produce Detector Output, Electronics,39:16, p 120-121. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(537)
GATE_FOR_200_MC_INTERVAL_TIMER_
Published:2009/7/16 1:36:00 Author:Jessie
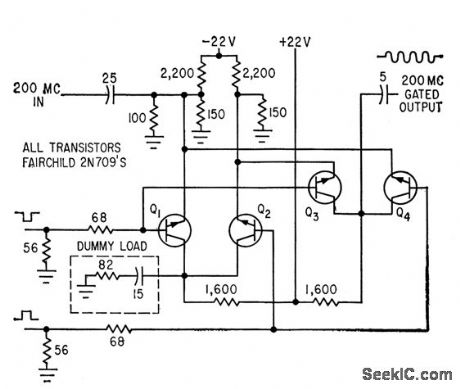
Two pairs of transistors can turn gate on or off in 1 nsec, from separate start and stop inputs. Only one transistor per pair conducts at a time.-C.S. Coffey, VHF Counter Measures Time Intervals Precisely, Electronics, 36:34, P 27-29. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(673)
RESISTOR_TRANSISTOR_NAND_NOR_GATE
Published:2009/7/16 1:36:00 Author:Jessie
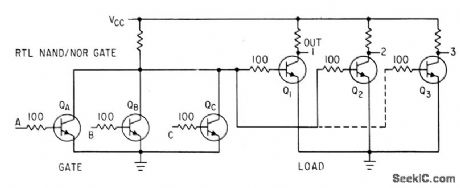
For integrated circuits, 100.ohm resistor in base lead of each transistor reduces waste curl rent, increases fan-out, and gives logic swing of 1 v.-A. E. Skoures, Choosing Logic for Microelectronics, Electronics, 36:40, p 23-26. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(548)
HANDWRITING_READER
Published:2009/7/16 1:35:00 Author:Jessie
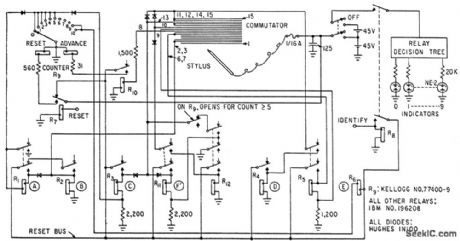
Spelled-out digits written with wire stylus on striated conductive surface are recognized by detecting risers, descenders, dots, word length, recrossings, and several other characteristics of spelled-out zero to nine, using only 12 relays, 8 diodes, and 10 neon indicator lamps. Accuracy is about 97% with the simple sequential logic used for recognition.-L. D. Harmon, Handwriting Reader Recognizes Whole Words, Electronics, 35:34, p 29-30. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(567)
HIGH_SPEED_TUNNEL_DIODE_BINARY
Published:2009/7/16 1:32:00 Author:Jessie
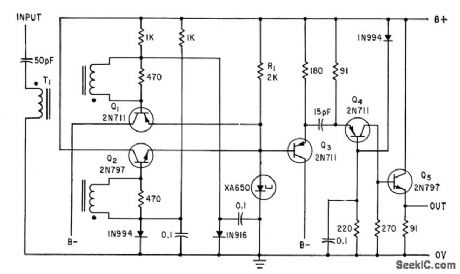
Tunnel diode with Q1-Q2, driven by series of positive or negative pulses at input repetition rates up to 140 Mc, can provide pulses capable of triggering successive pulse amplifier stages Q3, Q4, and Q5.-W. V. Harrison and R. S. Foote, Tunnel Diodes Increase Digital-Circuit Switching Speeds, Electronics, 34:32, p 154-156. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(626)
COUNTING_UP_TO_50_KC
Published:2009/7/13 23:20:00 Author:May
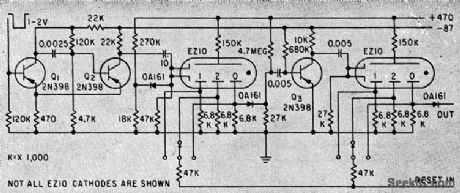

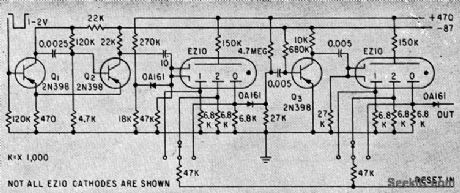
Input stage is Schmitt trigger Q1-Q2. Diode at input of interstage transistor amplifier Q3 dips base of cathode pulse.-K. Apel and P. Berweger, Miniature Gas-Filled Tubes For High-Speed Counting, Electronics, 33:8, p 46-47. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(497)
| Pages:164/471 At 20161162163164165166167168169170171172173174175176177178179180Under 20 |
Circuit Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit