
Analog Circuit
Index 17
WHEATSTONE_BRIDGE
Published:2009/6/22 22:35:00 Author:May


This circuit can be used to measure resistances. R7 is calibrated and fitted with an indicator dial, Lhen:
A frequency of 1 kHz for the audio oscillator is usually used. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(919)
PULSED_DOUBLE_HETEROSTRUCTURE_LASER_DRIVER
Published:2009/6/22 22:34:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(701)
IC_LASER_DIODE_DRIVER
Published:2009/6/22 22:33:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1226)
MUSIC_ON_HOLD_BOX
Published:2009/6/22 22:28:00 Author:May

U1, an LS3404 melody chip is activated when hold S1 is pressed, which causes SCRI to con-cluct and hold the telephone line via T1, R1, and LED1. The voltage across R1 and LED1 is used to activate the melody chip. Q1 and Q2 form a restart circuit to keep the melody chip going during hold. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1425)
LIGHT_BEAM_RECEIVER_AND_SOUND_EFFECTS_GENERATOR_FOR_LASER_PISTOLS
Published:2009/6/22 22:27:00 Author:May

Schematic diagram for light, beam amplifier and sound-effects generator (using a 555 timer IC and speaker). The light striking Q1 generates a siren-like sound. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(911)
TELEPHONE_RINGER
Published:2009/6/22 22:10:00 Author:May

Using an AMI chip P/N S2561, this telephone ringer can be powered line. Audio output is about 50 mW when powered from a 10-V source. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(2782)
HIGH_CURRENT_DRIVE_CIRCUIT_FOR_SINGLE_HETEROSTRUCTURE_LASER_DIODES
Published:2009/6/22 18:01:00 Author:May




The transistor is operated in the avalanche mode. You might need to try several 2N2222 devices before finding one that oscillates. R2 is adjusted for optimum oscillation. This supply provides pulse of 10 to 20 amps at about 50 ns. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(760)
SIMPLE_HARMONIC_DISTORTION_ANALYZER
Published:2009/6/22 17:54:00 Author:May




This simple circuit lets you accurately measure the total harmonic distortion(THD)using your true-RMS voltmeter.This THD circuit is somewhat different from the usual types: it can operate at the standard fre-quency of 1000 Hz, but it also is tunable from 970 Hz to 1030 Hz, and has an adjustable Q factor of 0.3 to over 50. Op-amp UI, a TLC272 CMOS unit, contains the two voltage-followers required to buffer the input to the bootstrapped twin-T notch filter. Tuning is accomplished by R1, R2, and R3, which are standard linear-taper slide pots ganged together by mounting them side-by-side and glu-ing their sliders together.The only other intportant construction hint is to use twisted pair at the cir-cuit's input and output.To calibrate the circuit, input a 1000-V RMS signal at 2000 Hz, set 51 to TEST, and adjust R7 for a reading of 0.99-V RMS on a true-RMS voltmeter at the output.To use the circuit, set 51 to TUNE, input a 1000-Hz sine-wave signal to the amplifier under test, and set the amplifier's output to the THD adapter and tune R1/R2/R3 for the lowest output signal.Then, set 51 to TEST and read the RMS voltage. To calculate the percent THD use: (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1435)
ANALOG_DE_GLITCH_CIRCUIT
Published:2009/6/19 5:13:00 Author:May




Low-frequency signals produced by transducers, measurement equipment, or data loggers often appear like the first waveform in the figure. The circuit shown operates as a tracking sample-hold, and the transients are replaced in the output by the stored value of the current signal at the instant of the transient.
The input signal is buffered and inverted by ICla, and the differentiated result shown at 2 ap-plied to the inputs of two comparators IC2-a and IC?-b. VR1 and VR2 set levels to prevent false or unnecessary operation. Either comparator output triggers the mono IC3 from positive or negative signal transients. When IC3 has not been triggered, TRI and TR2 'p' channel JFETs are on, and IClb operateb as an integrator with a high leakage, and tracks the input signal. When the mono is trig-gered as at 3, TRI and TR2 turn off and the previous signal value is held constant, as shown at 4. The resulting output waveform can then be easily filtered to remove the harmonics from the restoring step at the end of the mono period, if needed.
The criteria for successful operation are:
t2 > t1 (mono period longer than glitch)t2/T small (to optimize output waveform) Signal bandwidth Signal phase
The signal range is approximately ±5V, depending on the tfansient amplitude and polarity. The mono period shown is 100 mS, but this can be optimized in practical applications. The shorter the mono period in relation to the signal waveform, the better the quality of the result. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1138)
VIDEO_dc_RESTORE_CIRCUIT_
Published:2009/6/19 4:58:00 Author:May

This circuit restores the black level of a monochrome composite video signal to 0 V at the beginning of every horizontal line. This circuit is also useful with CCD scanners to set the black level. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1171)
SIMPLE_INVERTER
Published:2009/6/19 4:52:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(712)
VIDEO_FADER
Published:2009/6/19 4:50:00 Author:May

Using two LT1228 transconductance amplifiers in front of a current feedback amplifier forms a video fader. The ratio of the set currents into pin 5 determines the ratio of the inputs at the output. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(2)
1_kW_10_kHz_SINE_WAVE_INVERTER
Published:2009/6/19 4:49:00 Author:May

SCRs can produce considerable power at frequencies up to 30 kHz or more. This circuit can supply 1 kW at 10 kHz. The load is shown as an equivalent load, and practically this will be the primary of the transformer for isolation purposes. The power supply can be a 120-V bridge rectifier and filter combination. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(746)
POSITIVE_TO_NEGATIVE_dc_dc_INVERTER
Published:2009/6/19 4:48:00 Author:May
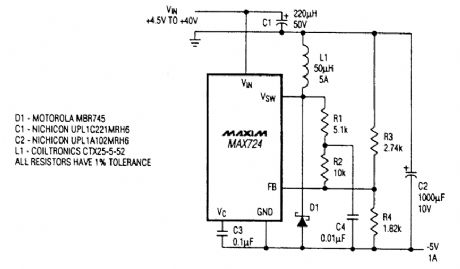
If a source of negative 5 Vdc is needed and only a positive supply is available, this circuit can be used. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(769)
TWO_INPUT_VIDEO_MULTIPLEX_CABLE_DRIVER
Published:2009/6/19 4:45:00 Author:May

CMOS logic levels select one of two video in-puts with this circuit. The op amps are Linear Technology LT1190s (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(715)
MULTIPLE_INPUT_VIDEO_MULTIPLEX_CABLE_DRIVER
Published:2009/6/19 4:44:00 Author:May



Using a Linear Technology LT1227, the mul-tiplex video amp uses logic levels to tum on and off selected inputs. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(673)
TIMER_ac_LINE_INTERFACE
Published:2009/6/19 4:43:00 Author:May

This circuit illustrates the use of an optoisolator to enable the control of a triac connected to the ac line and load, while maintaining dc and ac isolation between the ac line and the timer circuit. A 555 or other timer circuit can be used. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(3081)
ac_INTEGRATOR
Published:2009/6/19 4:41:00 Author:May

This op-antp circuit can be used with a wide variety of op amps. The values of Rf and Ri depend on gain, but will be 1 kΩ to 1 MΩ in most cases. Cf depends on the pole frequency needed. U1 is a 741-type op amp, etc. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1577)
SOIL_HEATER_FOR_PLANTS
Published:2009/6/19 4:41:00 Author:May

A TDA1024 electronic thermostat senses soil temperature via thermistor R6. The circuit uses zero-crossing switching of the heater. The heater is made of elastic-coated steel wire. P1 is used to set the temperature. The heater should have 2 Ω or more resistance and operate from the 9-V transformer. About 40W of heat is available. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(3636)
SIMPLE_INTEGRATOR
Published:2009/6/19 4:40:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(605)
| Pages:17/24 1234567891011121314151617181920Under 20 |
Circuit Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit



