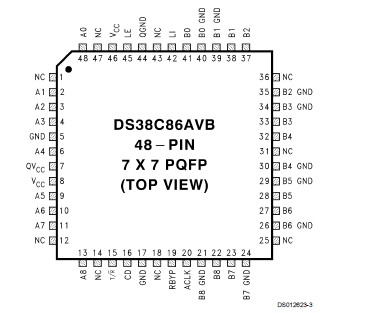
DS38C86A: Features: `>50% Less ICC then Bi-CMOS DS3886A`9-Bit inverting BTL latching transceiver`Meets IEEE 1194.1 Standard on Backplane Transceiver Logic (BTL)`Very low bus-port capacitance-3 pF typical`S...
floor Price/Ceiling Price
- Part Number:
- DS38C86A
- Supply Ability:
- 5000
Price Break
- Qty
- 1~5000
- Unit Price
- Negotiable
- Processing time
- 15 Days
SeekIC Buyer Protection PLUS - newly updated for 2013!
- Escrow Protection.
- Guaranteed refunds.
- Secure payments.
- Learn more >>
Month Sales
268 Transactions
Payment Methods
All payment methods are secure and covered by SeekIC Buyer Protection PLUS.

 DS38C86A Data Sheet
DS38C86A Data Sheet