Features: • Organization: 262,144 words × 18 bits
• Fast clock speeds to 200 MHz
• Fast clock to data access: 3.0/3.5/4.0 ns
• Fast OE access time: 3.0/3.5/4.0 ns
• Fully synchronous register-to-register operation
• Double-cycle deselect
• Asynchronous output enable control
• Available in 100-pin TQFP package
• Individual byte write and global write
• Multiple chip enables for easy expansion
• Linear or interleaved burst control
• Snooze mode for reduced power-standby
• Common data inputs and data outputs
• 3.3V core power supply
• 2.5V or 3.3V I/O operation with separate VDDQPinout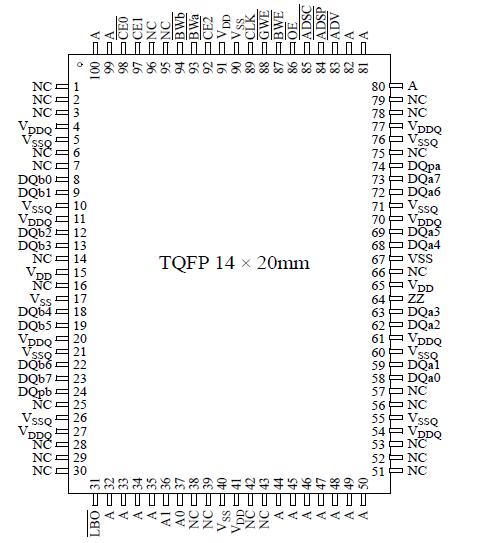 Specifications
Specifications
| Parameter |
Symbol |
Min |
Max |
Unit |
| Power supply voltage relative to GND |
VDD, VDDQ |
0.5 |
+4.6 |
V |
| Input voltage relative to GND (input pins) |
VIN |
0.5 |
VDD + 0.5 |
V |
| Input voltage relative to GND (I/O pins) |
VIN |
0.5 |
VDDQ + 0.5 |
V |
| Power dissipation |
Pd |
|
1.8 |
W |
| Short circuit output current |
IOUT |
|
20 |
mA |
| Storage temperature |
Tstg |
65 |
+150 |
|
| Temperature under bias |
Tbias |
65 |
+135 |
|
Stresses greater than those listed under "Absolute maximum ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions outside those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions may affect reliability.
DescriptionThe AS7C33256PFD18B is a high performance CMOS 4 Mbit synchronous Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) devices organized as 262,144 words × 18 bits and incorporate a pipeline for highest frequency on any given technology.
Timing for AS7C33256PFD18B is compatible with existing Pentium® synchronous cache specifications. This architecture is suited for ASIC, DSP, and PowerPC™1-based systems in computing, datacom, instrumentation, and telecommunications systems.
Fast cycle times of 5.0/6.0/7.5ns with clock access times (tCD) of 3.0/3.5/4.0 ns enable 200, 166 and 133 MHz bus frequencies.Three chip enable (CE) inputs permit easy memory expansion. Burst operation is initiated in one of two ways: the controller AS7C33256PFD18B address strobe (ADSC), or the processor address strobe (ADSP). The burst advance pin (ADV) allows subsequent internally generated burst addresses.
Read cycles are initiated with ADSP (regardless of WE and ADSC) using the new external address clocked into the on-chip address register when ADSP is sampled low, the chip enables are sampled active, and the output buffer is enabled with OE. In a read operation, the data of AS7C33256PFD18B accessed by the current address registered in the address registers by the positive edge of CLK are carried to the data-out registers AS7C33256PFD18B and driven on the output pins on the next positive edge of CLK. ADV is ignored on the clock edge that samples ADSP asserted, but is sampled on all subsequent clock edges. Address is incremented internally for the next access of the burst when ADV is sampled low and both address strobes are high. Burst mode is selectable with theLBOinput. With LBO unconnected or driven high, burst operations use an interleaved count sequence. WithLBOdriven low, AS7C33256PFD18B uses a linear count sequence.
Write cycles are performed by disabling the output buffers with OE and asserting a write command. A global write enable GWE writes all 18 bits regardless of the state of individual BW[a,b]inputs. Alternately, when GWE is high, one or more bytes of AS7C33256PFD18B may be written by asserting BWE and the appropriate individual byte BWn signals.
BWn is ignored on the clock edge that samples ADSP low, but AS7C33256PFD18B is sampled on all subsequent clock edges. Output buffers are disabled when BWnis sampled LOW regardless of OE. Data is clocked into the data input register when BWn is sampled low. Address is incremented internally to the next burst address if BWn and ADV are sampled low.AS7C33256PFD18B operates in doublecycle deselect feature during read cycles.
Read or write cycles may also be initiated with ADSC instead of ADSP. The differences between cycles initiated withADSCand ADSP are as follows:
• ADSP must be sampled high when ADSC is sampled low to initiate a cycle with ADSC.
•WE signals are sampled on the clock edge that samples ADSClow (and ADSP high).
•Master chip enable CE0 blocks ADSP, but not ADSC.
The AS7C33256PFD18B operates from a 3.3V supply. I/Os use a separate power supply that can operate at 2.5V or 3.3V. These devices are available in a 100-pin 14×20 mm TQFP package.

 AS7C33256PFD18B Data Sheet
AS7C33256PFD18B Data Sheet








