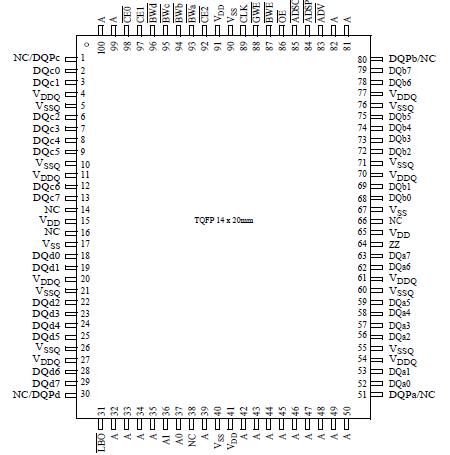
AS7C331MFT36A: Features: • Organization: 1,048,576 words × 32 or 36 bits• Fast clock to data access: 7.5/8.5/10 ns• FastOE access time: 3.5/4.0 ns• Fully synchronous flow-through operation&...
floor Price/Ceiling Price
- Part Number:
- AS7C331MFT36A
- Supply Ability:
- 5000
Price Break
- Qty
- 1~5000
- Unit Price
- Negotiable
- Processing time
- 15 Days
SeekIC Buyer Protection PLUS - newly updated for 2013!
- Escrow Protection.
- Guaranteed refunds.
- Secure payments.
- Learn more >>
Month Sales
268 Transactions
Payment Methods
All payment methods are secure and covered by SeekIC Buyer Protection PLUS.

 AS7C331MFT36A Data Sheet
AS7C331MFT36A Data Sheet