Features: • Organization: 2,097,152 words × 18 bits
• NTD™architecture for efficient bus operation
• Fast clock to data access: 7.5/8.5/10 ns
• Fast OE access time: 3.5/4.0 ns
• Fully synchronous operation
• Flow-through mode
• Asynchronous output enable control
• Available in 100-pin TQFP package
• Byte write enables
• Clock enable for operation hold
• Multiple chip enables for easy expansion
• 2.5V core power supply
• Self-timed write cycles
• Interleaved or linear burst modes
• Snooze mode for standby operationPinout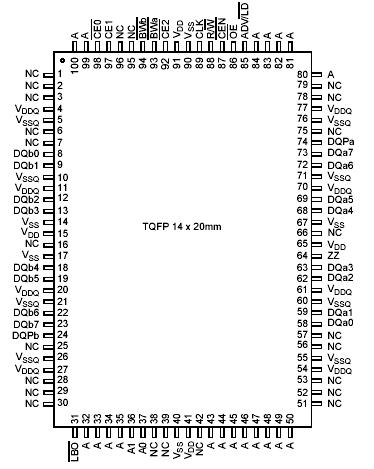 Specifications
Specifications
|
Parameter
|
Symbol
|
Min
|
Max
|
Unit
|
| Power supply voltage relative to GND |
VDD, VDDQ |
0.5 |
+4.6 |
V |
| Input voltage relative to GND (input pins) |
VIN |
0.5 |
VDD + 0.5 |
V |
| Input voltage relative to GND (I/O pins) |
VIN |
0.5 |
VDDQ + 0.5 |
V |
| Power dissipation |
PD |
|
1.8 |
W |
| DC output current |
IOUT |
|
20 |
mA |
| Storage temperature (plastic) |
Tstg |
65 |
+150 |
|
| Temperature under bias (Junction) |
Tbias |
65 |
+135 |
|
DescriptionThe AS7C252MNTF18A family is a high performance CMOS 32 Mbit synchronous Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) organized as 2,097,152 words × 18 bits and incorporates a LATE Write.
This variation of the 32Mb+ synchronous SRAM uses the No Turnaround Delay (NTD™) architecture, featuring an enhanced write operation that improves bandwidth over flowthrough burst devices. In a normal flowthrough burst device, the write data, command, and address are all applied to the device on the same clock edge. If a read command follows this write command, the system must wait for one 'dead' cycle for valid data to become available. This dead cycle can significantly reduce overall bandwidth for applications requiring random access or read-modify-write operations.
NTD™ devices use the memory bus more efficiently by introducing a write latency which matches the one-cycle flowthrough read latency. Write data is applied one cycle after the write command and address, allowing the read pipeline to clear. With NTD™, write and read operations can be used in any order without producing dead bus cycle.
Assert R/W low to perform write cycles. Byte write enable controls write access to specific bytes, or can be tied low for full 18 bit writes. Write enable signals, along with the write address, are registered on a rising edge of the clock. Write data is applied to the device one clock cycle later. Unlike some asynchronous SRAMs, output enable OE does not need to be toggled for write operations; it can be tied low for normal operations. Outputs go to a high impedance state when the device is de-selected by any of the three chip enable inputs.
Use the ADV (burst advance) input to perform burst read, write and deselect operations. When ADV is high, external addresses, chip select, R/W pins are ignored, and internal address counters increment in the count sequence specified by the LBO control. Any device operations, including burst, can be stalled using the CEN=1, the clock enable input.
The AS7C252MNTF18A operates with a 2.5V ± 5% power supply for the device core (V
DD). These devices are available in 100-pin TQFP package.

 AS7C252MNTF18A Data Sheet
AS7C252MNTF18A Data Sheet








