
Index 73
LOW_COST_pH_METER
Published:2009/6/25 20:40:00 Author:May

With guaranteed 1 pA input bias, the ICL 8007A is ideal as a pH meter or long term sample and hold. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1880)
NUCLEAR_PARTICLE_DETECTOR
Published:2009/6/25 5:14:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(655)
WIDEBAND_RADIATION_MONITOR
Published:2009/6/25 5:09:00 Author:May

A sensitive radiation monitor may be sim-ply constructed with a large-area photodiode and a quad operational amplifier. Replacing the glass window of the diode with Mylar foil wili shield it from light and infrared energy,enabbling it to respond to such nuclear radiation as alpha and beta particles and gamma rays. A4 integrates the output of A3 In order to drive amlcroammeter,Al microfarad capacitor isused in the integratingnetwork.A lower value,say,33 nanofarads,will make it possible todrive a small loudspeaker (50-hertz output signal) or light-emitting diode. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1377)
DOSAGE_RATE_METER
Published:2009/6/25 5:07:00 Author:May

A commercial diode is the detector in this highly accurate radiation monitor. The lowdrift FET-input op amp amplifies detector current to a usable level, and the chopper-stabilized amplifier then provides additional gain while minimizing any error caused by ambient-temperature fluctuations. Gain is adjusted so that the output voltage is 1% of incident radia-tion intensity in rads per minute; therefore voltage can be displayed on 3 1/2 digit DVM for direct reading of dosage rate. Output voltage from the monitor is linearly proportional to radiation intensity at the diode. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1314)
TTLLOGIC_TESTER
Published:2009/6/25 4:26:00 Author:May

Gates GI and G2 together with resistors RI and R2 form a simple voltage monitor that has a trip point of 1.4 volts. Gate G3 is simply an inverter. The display section of the tester consists of a common anode alphanumeric LED and current-limiting resistors. It indicates whether the input voltage is above or below 1.4 V, and displays a H or a L (for high or low logic-level) respectively. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(641)
CURRENT_MONITOR
Published:2009/6/25 3:31:00 Author:May
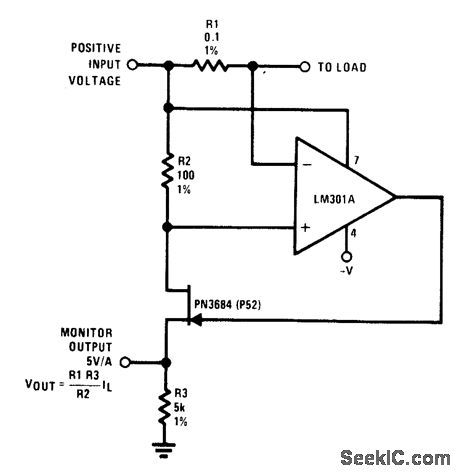
Circuit Notes
R1 senses current flow of a power supply. The JFET is used as a buffer because ID = Is; therefore the output monitor voltage accu-rately reflects the power supply current flow. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
NANOAMPERE_SENSING_CIRCUIT_WITH_100_MEGOHM_INPUT_IMPEDANCE
Published:2009/6/25 3:29:00 Author:May

Circuit Notes
The circuit may be used as a sensitive current detector or as a voltage detector having high input impedance. RI is set so that the voltage at point (A) is Vz to 3A volts below the level that fires the 2N494C. A small input cur-rent (Iin) of only 40 nanoamperes will charge C2 and raise the voltage at the emitter to the firing level. When the 2N494C fires, both capacitors, C1 and C2, are discharged through the 27 ohm resistor, which generates a positive pulse with sufficient amplitude to trigger a con-trolled rectifier (SCR), or other pulse sensitive circuitry. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
NANO_AMMETER
Published:2009/6/25 3:25:00 Author:May


The complete meter amplifier is a differen-tial current-to-voltage converter with input pro-tection, zeroing and full scale adjust provisions, and input resistor balancing for minimum offset voltage. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
PICO_AMMETER
Published:2009/6/25 3:22:00 Author:May

Circuit Notes
A very sensitive pico ammeter (-1V/pA) employs the amplifier in the inverting or cur-rent summing mode. Care must be taken to eliminate stray currents from flowing into the current summing mode. It takes approximately 5 for the circuit to stabilize to within 1% of its final output voltage after a step function of input current has been applied. The internal diodes CR1 and CR2 together with external resistor R1 to protect the input stage of the amplifier from voltage transients. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(3668)
AMMETER
Published:2009/6/25 3:16:00 Author:May

Circuit Notes
Current meter ranges from 100 pA to 3 mA full scale. Voltage across input is 100μV at lower ranges rising to 3 mV at 3 mA. The buffers on the op amp are to remove ambiguity with high-current overload, The output can also drive a DVM or a DPM. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(3071)
LIQUID_LEVEL_DETECTOR
Published:2009/6/25 2:52:00 Author:May

When liquid level reaches both probes, alarm is tumed on. When water level recedes it goes off. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(663)
LIQUID_LEVEL_DETECTOR(LATCHING)
Published:2009/6/25 2:48:00 Author:May

Alarm is actuated when liquid level is above the probes and remains activated even if the level drops below the probes. This latching action lets you know that the pre-set level has been reached or exceeded sometime in the past. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(476)
HIGH_LEVEL_WARNING_DEVICE
Published:2009/6/25 2:45:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(812)
3LIGHT_METER
Published:2009/6/25 2:27:00 Author:May

This light meter has an eight-decade range. Bias current compensation can give input current resolution of better than ±2 pA over 15 ℃ to 55℃. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
2LIGHT_METER
Published:2009/6/25 2:25:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
1LIGHT_METER
Published:2009/6/25 2:24:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(609)
LOGARITHMIC_LIGHT_METER_CIRCUIT
Published:2009/6/25 2:22:00 Author:May

The meter reading is directly proportional to the logarithm of the input light power. The logarithmic circuit behavior arises from the nonlineardiode pnjunction current/voltage relationship. The diode in the amplifier output prevents output voltage from becoming nega-tive (thereby pegging the meter), which may happen at low lightlevels due to amplifier bias currents. R1 adjusts the meter full-scale deflection, enabling the meter to be calibrated. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1159)
LINEAR_LIGHT_METER_CIRCUIT
Published:2009/6/25 2:21:00 Author:May

This circuit uses a low-input-bias op amp to give a steady dc indication of light level. To reduce circuit sensitivity to light, R1 can be reduced, but should not be less than 100 K. The capacitor values in the circuit are chosen to provide a time constant sufficient to filter high-frequency light variations that might arise, for example, from fluorescent lights. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1336)
PRECISION_DUAL_LIMIT_GO_NO_GO_TESTER
Published:2009/6/25 1:53:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
MICROPOWER_DOUBLE_ENDED_LIMIT_DETECTOR
Published:2009/6/25 1:47:00 Author:May

The detector uses three sections of an L144 and a DC4011 type CMOS NAND gate to make a very low power voltage monitor. If the input voltage, VIN, is above VHIGH or below VLOW, the output will be a logical high. If (and only if) the input is between the limits will the output be low. The 1 megohm resistors RI, R2, R3, and R4 translate the bipolar ±10V swing of the op amps to a 0 to 10V swing acceptable to the ground-referenced CM0S logic. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(584)
| Pages:73/101 At 206162636465666768697071727374757677787980Under 20 |
Circuit Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit




