
Basic Circuit
Index 344
SAMPLING_RATE_PHASE_LOCK
Published:2009/6/23 2:44:00 Author:May



Most digital scopes have record lengths that are power of 2 (e.g., 1024 points) and sampling rates constrained to a 1-2-5 sequence. This can lead to measurement errors on power-line waveforms because an integral number of line cycles can't be captured. Digital scopes that calculate measurements, such as the rms level, across the entire record will be in error.One solution to this problem is to phase-lock the scope's sampling rate to the line frequency by exploiting the external clock input found on some digital scopes. Phase-locking the sampling to line frequency also tracks variations in the power-line frequency.A 9- or 12-Vac wall transformer provides the circuit's power and the frequency reference. The negative output of the diode bridge refines the circuit ground. The 78L05 regulator provides the +5 V supply for the three ICs. R3 and C2 create a low-pass filter on the half-cycles from one of the floating transformer outputs. R3 also limits the current into the internal diode clamps of the inverter gate.The inverter output becomes the power-line frequency reference and is one input (SIG in to the phase comparator) of the Signetics 74HC4046A phase-locked loop (PLL). The 74HC4040 divides the PLL output frequency by 1024 and feeds the divided clock back to the other PLL phase-comparator input (COMP in). The phase-comparator output (PC2) is filtered and drives the PLL's control voltage (VCO in) so that the output frequency is 1024 times the reference frequency.With the loop filter shown, the output frequency locks to the line frequency in about 10 s. The oscillator is locked to both 50- and 60-Hz inputs using a 74HC4046A and the values shown for resis-tors RI and R2 and capacitor C1.The output signal is buffered and sent to the scope's external clock input, which is typically a TTL-compatible input. A different tap from the 74HC4040 can be selected to control the number or cycles captured in one scope record. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1278)
MUTING_CIRCUIT
Published:2009/6/23 2:43:00 Author:May

The circuit operates as follows: The signal is input to Vin and a dc control voltage is applied to VC. Vbias determines the desired bias point current. Assuming the following component and voltage values:
VCC=7.6 VdcVbias=1 VdcVin=1Vp-p,ac signal centered about 3.8 Vdc biasRL=2kΩRE=200kΩRE1=2kΩ
Q3 bias current is 1 mA, and dc output voltage is about 5.8Vwith an ac gain of about -1, Q1 and Q2 form a current switch and Q3 acts as a constant current source.For unmuted operation, Vc=0Vdc, and all of the bias current flows through Q1. Consequently, the circuit operates as a normal common emitter stage, with ac gain=-RL/RE1,. When Vc=5Vdc, all of the bias current flows through Q2, reducing the signal gain to zero. However, because the same dc current flows through RL, in both cases(unmuted and muted), the bias point at the output remains fixed. The Cc/RE1network is required to bypass the Q3 current source(which is a high impedance)to achieve alow ac impedance at the emitter of the Q1 common emitter stage during unmuted oper-ation. Cc is chosen to be a short circuit at signal frequencies of interest. The circuit works best if the Q1 and Q2 pair is matched. Typical change in the output dc voltage from unmuted to muted condi-tion is <5 mVdc.
RL,RE, and Vbias are chosen for desired dc operating conditions and signal dynamic range. Vbias, can be generated via a VCC voltage divider. The signal at Vin, can be ac coupled, but a bias circuit must be added to Q1's base to generate a dc component. RE1 is chosen for desired ac gain. Vin must be cen-tered about a dc component, and, to assure proper switching action, VCTRL, must be higher than Vin, by an amount greater than one VBE drop. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(769)
The internal block circuit diagram of LA7680 IC
Published:2011/6/23 2:45:00 Author:Ecco | Keyword: internal block , IC

LA7680 is a small TV signal processing monolithic integrated circuit which is produced by Sanyo company of Japan. It is widely used in various types of domestic and imported large screen color TV. The featuresand functionsLA7680 IC contains images and audio amplifier circuit, color demodulation circuit, the luminance signal processing circuit, line scanning and field scanning small signal processing circuit, voltage controlled oscillator circuit, PAL / NTSC standard switch circuit, sync separator circuit and AFT control circuit. The IC's internal circuit block diagram is shown as the chart.
The internal block circuit diagram of LA7680 IC is shown as the chart. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(4920)
SCOPE_VOLTAGE_CURSOR_ADAPTER
Published:2009/6/23 2:39:00 Author:May

The voltage cursor adapter superimposes horizontal cursor lines on the top and bottom of the waveform-a kind of electronic calipers-to perrrtit direct readout of the voltage value. The cursor lines extend across the entire screen. The MC78L12 voltage regulator (IC1) supplies regulated 12 Vdc to the rest ofthe circuit. The ICM7555 timer (IC2) drives the CD4066B, a CMOS bilateral switch (IC3). This drive frequency can either be a normal frequency (NORM) of 100 Hz or a low-frequency (LO-F) of 10 kHz, depending on the setting of switch S1. Set S1 to LO-F for inputs below 500 Hz.The dc reference voltage supplied to pin 3 of IC3 is set by R3, a 10-turn, 5000-Ω precision potentiometen The voltage can be read directly from a turns counter dial coupled directly to the potentiometer's wiper. The accuracy of this reading can be 1% or better. Trimmer potentiometer R1 permits the voltage to R3 to be calibrated to precisely 10 V.The circuit is calibrated by setting the digital reading on the turns counter of R3 to the full clockwise position and adjusting R1 for a reading of 10 V at the wiper of R3 with a digital voltmeter.Bilateral switch IC3 converts the dc reference to a square wave with exactly the same wiper amplitude. The square-wave output appears on common pins 4, 9, and 10 of IC3 and coaxial plug PL1. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1015)
BOOTSTRAP_CIRCUIT
Published:2009/6/23 2:33:00 Author:May

Bootstrapping the substrate of a JFET amplifier reduces the distortion caused by the nontinlearity of the JFET input capacitance. In the figure, a second feedback divider bootstraps the substrate of U1. With R1=500 kΩ (source im-pedance), THD at 10 kHz was reduced an order of magnitude. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1497)
SIMMAX card reader principle diagram
Published:2011/7/25 3:05:00 Author:Ecco | Keyword: SIMMAX , card reader, principle diagram
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1611)
The design of dot matrix LED electronic display
Published:2011/7/25 3:04:00 Author:Ecco | Keyword: design , dot matrix, LED , electronic display

H1 ~ H16 can choose 8550. 2756 is available in E2PROM.
(View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(2178)
HF_VFO_CIRCUIT
Published:2009/6/23 2:22:00 Author:May

This typical HF VFO circuit has several stability-enhancing features, including well-chosen capacitor types. The frequency of the VFO is approximately 2π (C1 + C2 + C3) L1. L1 should be an aircore type coil, rigidly mounted, with high (>200 value) value of Q. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
CAPACITOR_HYSTERESIS_COMPENSATOR
Published:2009/6/23 2:22:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
COMPLEMENTARY_OR_BILATERAL_ac_EMITTER_FOLLOWER_CIRCUIT
Published:2009/6/23 2:20:00 Author:May

This noninverting circuit uses a pair of com-plementary npn (2N3904) and pnp (2N3906) transistors. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
PULSE_ECHO_DRIVER
Published:2009/6/23 2:19:00 Author:May

This pulse-echo driver uses the OPA2662 dual operational transconductance amplifier(OTA)from Burr-Brown(the reeeive circuitry isn't shown). The OTA is preferable over an op amp for driv-ing low impedances because it provides a current output rather than a voltage output.Ultrasonic pulse-echo applications often incorporate a transformer-coupled crystal to obtain a high-voltage pulse because the echo can be orders of magnitude smaller in amplitude. The trans-former turns ratio also provides tuning at the resonant frequency of the crystal, which usually means a relatively low-impedance primary winding.An operational transconductance amplifier(OTA)is preferred over an op amp to drive such a low impedance. One particular application involves a pulse-echo driver circuit using the OPA2662. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1531)
OCTAVE_EQUALIZER
Published:2009/6/23 2:18:00 Author:May

This circuit is one section of an octave equalizer used in audio systems. The table shows the val-ues of C1 and C2 that are needed to achieve the given center frequencies. This circuit is capable of 12 dB boost or cut, as determined by the position of R2. Because of the low input bias current of th,e OP-08, the resistors could be scaled up by a factor of 10, and thereby reduce the values of C1 and C2 at the low-frequency end. In addition, 10 sections will only draw a combined supply current of 6 mA maximum. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(873)
JFET_CHOPPER_CIRCUIT
Published:2009/6/23 2:14:00 Author:May
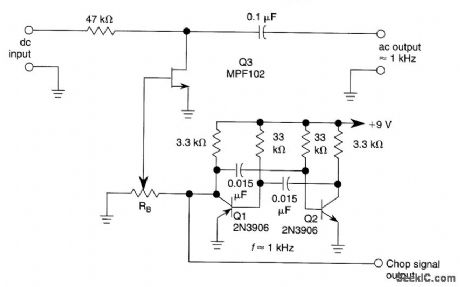
A JFET (MPF102) is used to chop a dc signal for amplification in an ac coupled amplifien Q3 is the chopper element and Q1-Q2 forms the multivibrator to derive a chopping signal. R, sets the bias on the FET to keep the drive to MPF102 as low as possible. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(2253)
PRECISION_POWER_BOOSTER
Published:2009/6/23 2:13:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(694)
BASIC_LATCH_CIRCUITS
Published:2009/6/23 2:30:00 Author:Jessie

Some simple latches and alternate action circuits. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(634)
500_ksps_8_CHANNEL_DATA_DCQUISITION_CIRCUT
Published:2009/6/23 2:10:00 Author:May

The high input impedance of the LTC1278 allows multiplexing without abuffer amplifier. Both sin-gle channel and multiplexed high-speed data acquisition systems benefit from the LTC1278/LTC1279's dynamic conversion performance. The 1.6-μs and 1.4-μs conversion and 200-ns and 180-ns S/H acquisition times enable the LTC1278/LTC1279 to convert a 500 ksps and 600 ksps, respectively. The figure shows a 500-ksps 8-channel data acquisition system. The LTC1278's high input impedance eliminates the need for a buffer amplifier between the multiplexer's output and the Adc's input. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
PROGRAMMABLE_GAIN_NONINVERTINGAMPLIFIER_WITH_SELECTABLE_INPUTS
Published:2009/6/23 2:08:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
PRECISION_PROCESS_CONTROL_INTERFACE
Published:2009/6/23 2:03:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
1_dB_PAD
Published:2009/6/23 2:03:00 Author:May

The 1-dB pad is useful as a termination in RF work to limit possible mismatch range between system blocks, etc. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
DISCRETE_CURRENT_BOOSTER
Published:2009/6/23 2:02:00 Author:May
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
| Pages:344/471 At 20341342343344345346347348349350351352353354355356357358359360Under 20 |
Circuit Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit





