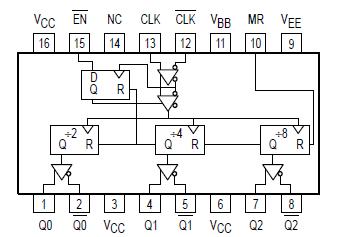
100EL34: PinoutDescriptionThe MC10/100EL34 is a low skew ÷2, ÷4, ÷8 clock generation chip designed explicitly for low skew clock generation applications. The internal dividers are synchronous to each other, ...
floor Price/Ceiling Price
- Part Number:
- 100EL34
- Supply Ability:
- 5000
Price Break
- Qty
- 1~5000
- Unit Price
- Negotiable
- Processing time
- 15 Days
SeekIC Buyer Protection PLUS - newly updated for 2013!
- Escrow Protection.
- Guaranteed refunds.
- Secure payments.
- Learn more >>
Month Sales
268 Transactions
Payment Methods
All payment methods are secure and covered by SeekIC Buyer Protection PLUS.

 100EL34 Data Sheet
100EL34 Data Sheet