Electrical Equipment Circuit
Index 76
SIGHT_N’SOUND_METRONOME
Published:2009/6/25 21:03:00 Author:Jessie

Precise, adjustable control of beats per minute from a largo of 18 to a frenzied, high presto of 500. These beiats are produced acoustically through a speaker. A light flashes at the same rate. When SW1 is closed, C1 begins to charge through R1 and R2. C1 will eventually reach a voltage at which the emitter of unijunction transistor is switched on, dumping the energy stored in C1 into an 8 ohm speaker. To produce a distinct plop , brief pulses across T2 secondary drive Q2 into conduction. The extra gain of Q3 and Q4 are sufficient to briefly switch L1 on, then off, as the pulse wave passes. Capacitor C2 stretches the pulse slightly to overcome the thermal inertia of the lamp, so that a bright flash occurs. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(998)
PHASE_METER
Published:2009/6/25 20:55:00 Author:Jessie
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1024)
108_MHz_FSK_DECODER
Published:2009/6/25 20:54:00 Author:Jessie
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(849)
MINIMUM_COMPONENT_TACHOMETER
Published:2009/6/25 20:54:00 Author:Jessie
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1103)
SENSITIVE_RE_VOLTMETER
Published:2009/6/25 20:53:00 Author:Jessie

This circuit measures RF voltages beyond 200 MHz and up to about 5 V. The diode should be mounted in a remote probe, close to the probe tip. Sensitivity is excellent and voltages less than 1 V peak can be easily measured. The unit can be calibrated by connecting the input to a known level of RF voltage, such as a calibrated signal generator, and setting the calibrate control. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(975)
VIBRATION_METER
Published:2009/6/25 20:52:00 Author:Jessie
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1993)
SCA_BACKGROUND_MUSIC_DECODER
Published:2009/6/25 20:52:00 Author:Jessie

A resistive voltage divider is used to es-tablish a bias voltage for the input (pins 2 and 3). The demodulated (multiplex) FM signal is fed to the input through a two-stage high-pass filter, both to effect capacitive coupling and to attenuate the strong signal o f the regular chan-nel. A total signal amplitude, between 80 mV and 300 mV, is required at the input. Its source should have an impedance of less than 10,000 ohms. The Phase Locked Loop is tuned to 67 kHz with a 5000 ohm potentiometer; only ap-proximate tuning is required, since the loop will seek the signal. The demodulated output (pin 7) passes through a three-stage low-pass filter to provide de-emphasis and attenuate the high-frequency noise which often accompanies SCA transmission. The demodulated output signal is in the rder of 50m V and the frequency response extends to 7 kHz. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
LINEAR_VARIABLE_DIFFERENTIAL_TRANSFORMER(LVDT)MEASURING_GAUGE
Published:2009/6/25 20:52:00 Author:Jessie
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(2842)
LINEAR_VARIABLE_DIFFFERENTIAL_TRANSFORMER(LVDT)DRIVER_DEMODULATOR
Published:2009/6/25 20:51:00 Author:Jessie
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
SOUND_LEVEL_MONITOR
Published:2009/6/25 20:50:00 Author:Jessie

Loudness detector consists of a 555 IC wired as a Schmitt trigger. The output changes state—from high to low—whenever the input crosses a certain voltage. That threshold voltage is established by the setting of R4. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
PEAK_LEVEL_INDICATOR
Published:2009/6/25 20:49:00 Author:Jessie

The LED is normally lit, but it will be briefly extinguished if the input exceeds a preset (by RV1) level. A possible application is to monitor the output voltage across a loudspeaker; the LED will flicker with large signals. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
DIODE_TESTER
Published:2009/6/25 20:48:00 Author:Jessie

The circuit tests whether or not a diode is open, shorted, or functioning correctly. If lamp A lights, the diode under test is functional. When lamp B is lit, the diode is good but connected backwards. When both lamps are lit, the diode is shamed, and it is open if neither lamp is lit. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1226)
100_K_MEGOHM_DC_PROBE
Published:2009/6/25 4:10:00 Author:Jessie

A 741 op amp is used with t00% ac and dc feedback to provide a typical input impedance of 1011 ohm and unity gain. To avoid hum and rf pickup the input leads should be kept as short as possible and the circuit should be mounted in a small grounded case. Output leads may belong since the output impedance of the circuit is a fraction of an ohm. With no input the output level is indeterminate. Including RI in the cir-cuit through lowers the input impedance to 22 M. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1054)
RF_PROBE_FOR_VOM
Published:2009/6/25 4:09:00 Author:Jessie

This probe makes possible relative measurements of rf voltages to 200 MHz on a 20,000 ohms-per-volt multimeter.Rf voltage must not exceed the breakdown rating of the IN4149-approximately 100 V. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(950)
CURRENT_MONITOR
Published:2009/6/25 3:31:00 Author:Jessie
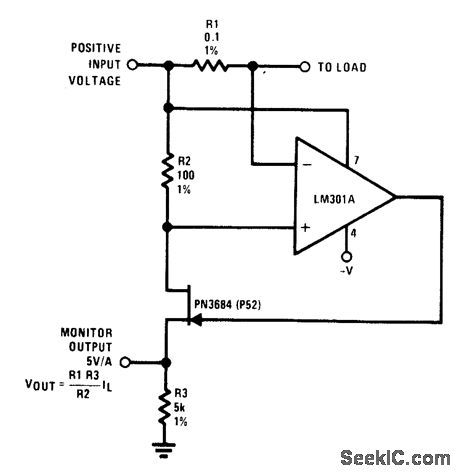
Circuit Notes
R1 senses current flow of a power supply. The JFET is used as a buffer because ID = Is; therefore the output monitor voltage accu-rately reflects the power supply current flow. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1379)
NANOAMPERE_SENSING_CIRCUIT_WITH_100_MEGOHM_INPUT_IMPEDANCE
Published:2009/6/25 3:29:00 Author:Jessie

Circuit Notes
The circuit may be used as a sensitive current detector or as a voltage detector having high input impedance. RI is set so that the voltage at point (A) is Vz to 3A volts below the level that fires the 2N494C. A small input cur-rent (Iin) of only 40 nanoamperes will charge C2 and raise the voltage at the emitter to the firing level. When the 2N494C fires, both capacitors, C1 and C2, are discharged through the 27 ohm resistor, which generates a positive pulse with sufficient amplitude to trigger a con-trolled rectifier (SCR), or other pulse sensitive circuitry. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1163)
NANO_AMMETER
Published:2009/6/25 3:25:00 Author:Jessie


The complete meter amplifier is a differen-tial current-to-voltage converter with input pro-tection, zeroing and full scale adjust provisions, and input resistor balancing for minimum offset voltage. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(2450)
CRYSTAL_CONTROLLED_OSCILLATOR
Published:2009/6/25 2:35:00 Author:Jessie


Circuit Notes
This circuit oscillates without the crystal. With the crystal in the circuit, the frequency will be that of the crystal. The circuit has good starting characteristics even with the poorest crystals. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
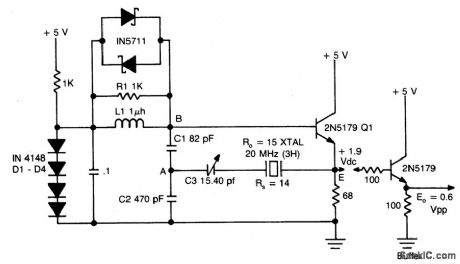
COLPITTS_OSCILLATOR
Published:2009/6/25 2:32:00 Author:Jessie

Circuit Notes
This circuit will operate with fundamental-mode crystals in the range of 1MHz to 20 MHz,Feedback is controlled by capacitor voltage divider C2/C3.The rfvoltageacross the emitter resistor provides the basic feedback signal. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(555)
BUTLER_EMITTER_FOLLOWER_OSCILLATOR(20_MHz)
Published:2009/6/25 2:26:00 Author:Jessie
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1032)
| Pages:76/126 At 206162636465666768697071727374757677787980Under 20 |
Circuit Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit