Features: ·Fully Supports Provisions of IEEE 1394-1995 Standard for High-Performance Serial Bus† and the P1394a Supplement
·Fully Interoperable with FireWireTM and i.LINKTM Implementation of IEEE Std 1394
·Fully Compliant With OpenHCI Requirements
·Provides Four P1394a Fully-Compliant
Cable Ports at 100/200/400 Megabits per Second (Mbits/s)
·Full P1394a Support Includes: Connection Debounce, Arbitrated Short Reset, Multispeed Concatenation, Arbitration Acceleration, Fly-By Concatenation, Port Disable/Suspend/Resume
·Extended Resume Signaling for Compatibility With Legacy DV Devices
·Power-Down Features to Conserve Energy in Battery-Powered Applications Include: Automatic Device Power-Down during Suspend, Device Power-Down Terminal, Link Interface Disable Via LPS, and Inactive Ports Powered-Down
·Ultra Low-Power Sleep Mode
·Node Power Class Information Signaling for System Power Management
·Cable Power Presence Monitoring
·Cable Ports Monitor Line Conditions for Active Connection to Remote Node
·Register Bits Give Software Control of Contender Bit, Power Class Bits, Link Active Control Bit and P1394a Features
·Data Interface to Link-Layer ControllerThrough 2/4/8 Parallel Lines at 49.152 MHz
·Interface to Link-Layer Controller Supports Low-Cost TITMBus-Holder Isolation and Optional Annex J Electrical Isolation
·Interoperable With Link-Layer Controllers Using 3.3-V and 5-V Supplies
·Interoperable With Other Physical Layers (PHYs) Using 3.3-V and 5-V Supplies
·Low-Cost 24.576-MHz Crystal Provides Transmit, Receive Data at 100/200/400 Mbits/s, and Link-Layer Controller Clock at 49.152 MHz
·Incoming Data Resynchronized to Local Clock
·Logic Performs System Initialization and Arbitration Functions
·Encode and Decode Functions Included for Data-Strobe Bit Level Encoding
·Separate Cable Bias (TPBIAS) for Each Port
·Single 3.3-V Supply Operation
·Low-Cost High-Performance 80-Pin TQFP (PFP) Thermally Enhanced Package
Pinout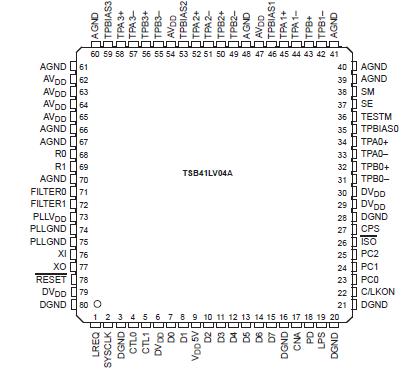 SpecificationsSupply voltage range, VCC (see Note 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.3 V to 4 V
SpecificationsSupply voltage range, VCC (see Note 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.3 V to 4 V
Input voltage range, VI (see Note 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5 V to VCC + 0.5 V
5-V tolerant I/O supply voltage range, VDD5V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.3 V to 5.5 V
5-V tolerant input voltage range, VI(5V) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5 V to VDD5V + 0.5 V
Output voltage range at any output, VO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5 V to VDD + 0.5V
Electrostatic discharge (see Note 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . HBM: 2 kV, MM: 200 V
Continuous total power dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Dissipation Rating Table
Operating free air temperature,TA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0 to 70
Storage temperature range, Tstg . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65 to 150
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
NOTES:
1. All voltage values, except differential I/O bus voltages, are with respect to network ground.
2. HBM is Human Body Model, MM is Machine Model.DescriptionThe TSB41LV04A requires only an external 24.576 MHz crystal as a reference. An external clock may be provided instead of a crystal. An internal oscillator drives an internal phase-locked loop (PLL), which generates the required 393.216 MHz reference signal. This reference signal is internally divided to provide the clock signals used to control transmission of the outbound encoded strobe and data information. A 49.152 MHz clock signal is supplied to the associated LLC for synchronization of the two chips and is used for resynchronization of the received data. The power-down (PD) function, when enabled by asserting the PD terminal high, stops operation of the PLL.
The TSB41LV04A supports an optional isolation barrier between itself and its LLC. When the ISO input terminal is tied high, the LLC interface outputs behave normally. When the ISO terminal is tied low, internal differentiating logic is enabled, and the outputs are driven such that they can be coupled through a capacitive or transformer galvanic isolation barrier as described in Annex J of IEEE Std 1394-1995 and in the P1394a Supplement (section 5.9.4) (hereafter referred to as Annex J type isolation). To operate with TI bus holder isolation the ISO terminal on the PHY must be high.
Data bits to be transmitted through the cable ports are received from the LLC on two, four or eight parallel paths
(depending on the requested transmission speed) and are latched internally in the TSB41LV04A in synchronization with the 49.152 MHz system clock. These bits are combined serially, encoded, and transmitted at 98.304, 196.608, or 393.216 Mbits/s (referred to as S100, S200, and S400 speed respectively) as the outbound data-strobe information stream. During transmission, the encoded data information is transmitted differentially on the TPB cable pair(s), and the encoded strobe information is transmitted differentially on the TPA cable pair(s).
During packet reception the TPA and TPB transmitters of the receiving cable port are disabled, and the receivers for that port are enabled. The encoded data information is received on the TPA cable pair, and the encoded strobe information is received on the TPB cable pair. The received data-strobe information is decoded to recover the receive clock signal and the serial data bits. The serial data bits are split into two, four, or eight bit parallel streams (depending upon the indicated receive speed), resynchronized to the local 49.152 MHz system clock and sent to the associated LLC. The received data is also transmitted (repeated) on the other active (connected) cable ports.
Both the TPA and TPB cable interfaces incorporate differential comparators to monitor the line states during initialization and arbitration. The outputs of these comparators are used by the internal logic to determine the arbitration status. The TPA channel monitors the incoming cable common-mode voltage. The value of this common-mode voltage is used during arbitration to set the speed of the next packet transmission. In addition, the TPB channel monitors the incoming cable common-mode voltage on the TPB pair for the presence of the remotely supplied twisted-pair bias voltage.
During packet reception the TPA and TPB transmitters of the receiving cable port are disabled, and the receivers
for that port are enabled. The encoded data information is received on the TPA cable pair, and the encoded strobe information is received on the TPB cable pair. The received data-strobe information is decoded to recover the receive clock signal and the serial data bits. The serial data bits are split into two, four, or eight bit parallel treams (depending upon the indicated receive speed), resynchronized to the local 49.152-MHz system clock and sent to the associated LLC. The received data is also transmitted (repeated) on the other active (connected) cable ports.
Both the TPA and TPB cable interfaces incorporate differential comparators to monitor the line states during initialization and arbitration. The outputs of these comparators are used by the internal logic to determine the arbitration status. The TPA channel monitors the incoming cable common-mode voltage. The value of this common-mode voltage is used during arbitration to set the speed of the next packet transmission. In addition, the TPB channel monitors the incoming cable common-mode voltage on the TPB pair for the presence of the remotely supplied twisted-pair bias voltage.

 TSB41LV04A Data Sheet
TSB41LV04A Data Sheet








