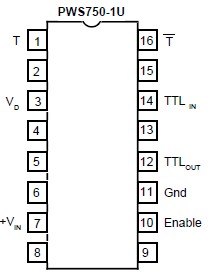
PWS750: Features: 100% TESTED FOR HIGH-VOLTAGE BREAKDOWNCOMPACT-SURFACE MOUNTMULTICHANNEL OPERATION5V OR 15V INPUT OPTIONSFLEXIBLE USE WITH PWS740/PWS745 COMPONENTSApplicationINDUSTRIAL PROCESS CONTROL EQUI...
floor Price/Ceiling Price
- Part Number:
- PWS750
- Supply Ability:
- 5000
Price Break
- Qty
- 1~5000
- Unit Price
- Negotiable
- Processing time
- 15 Days
SeekIC Buyer Protection PLUS - newly updated for 2013!
- Escrow Protection.
- Guaranteed refunds.
- Secure payments.
- Learn more >>
Month Sales
268 Transactions
Payment Methods
All payment methods are secure and covered by SeekIC Buyer Protection PLUS.

 PWS750 Data Sheet
PWS750 Data Sheet