Logic Family
:
Number of Bits
:
Counting Method
:
Counting Sequence
:
Operating Supply Voltage
:
Operating Temperature Range
:
Package / Case
:
Counter Type
: Binary Counters
Packaging
: Tube
Features: • Synchronous reversible 4-bit counting
• Asynchronous parallel load capability
• Asynchronous reset (clear)
• Cascadable without external logicPinout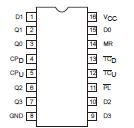 Specifications
Specifications
SYMBO |
PARAMETER |
RATING |
UNIT |
VCC |
Supply voltage |
0.5 to +7.0 |
V |
VIN |
Input voltage |
0.5 to +7.0 |
v |
IIN |
Input current |
30 to +5.0 |
mA |
VOUT |
Voltage applied to output in High output state |
0.5 to +VCC |
v |
IOUT |
Current applied to output in Low output state |
40 |
mA |
amb |
Operating free-air temperature range |
0 to +70 |
°C |
Tstg |
Storage temperature |
65 to +150 |
°C |
DescriptionThe 74F193 is a 4-bit synchronous up/down counter in the binary mode. Separate up/down clocks, CPU and CPD respectively, simplify operation. The outputs change state synchronously with the Low-to-High transition of either clock input. If the CPU clock is pulsed while CPD is held High, the 74F193 will count up. If CPD clock is pulsed while CPU is held High, the device will count down. The device can be cleared at any time by the asynchronous reset pin. 74F193 may also be loaded in parallel by activating the asynchronous parallel load pin.
Inside the 74F193 are four master-slave JK flip-flops with the necessary steering logic to provide the asynchronous reset, asynchronous preset, load, and synchronous count up and count down functions.
Each 74F193 flip-flop contains JK feedback from slave to master, such that a Low-to-High transition on the CPD input will decrease the count by one, while a similar transition on the CPU input will advance the count by one.One clock should be held High while counting with the other, because the circuit will either count by twos or not at all, depending on the state of the first JK flip-flop, which cannot toggle as long as either clock input is Low. Applications requiring reversible operation must make the reversing decision while the activating clock is High to avoid erroneous counts.
The Terminal Count Up (TCU) and Terminal Count Down (TCD) outputs are normally High. When the 74F193 circuit has reached the maximum count state of 15, the next High-to-Low transition of CPU will cause TCU to go Low. TCU will stay Low until CPU goes High again, duplicating the count up clock, although delayed by two gate delays. Likewise, the TCD output will go Low when the circuit is in the zero state and the CPD goes Low. The TC outputs can be used as the clock input signals to the next higher order circuit in a multistage counter, since they duplicate the clock waveforms.

 N74F193D Data Sheet
N74F193D Data Sheet







