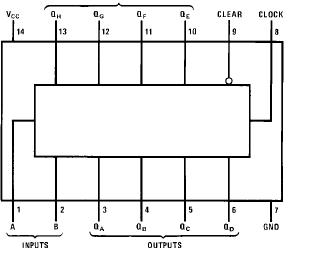
MM74C164: Features: · Supply voltage range: 3V to 15V· Tenth power TTL compatible: drive 2 LPTTL loads· High noise immunity: 0.45 VCC (typ.)· Low power: 50 nW (typ.)· Medium speed operation: 0.8 MHz (typ.) wi...
floor Price/Ceiling Price
- Part Number:
- MM74C164
- Supply Ability:
- 5000
Price Break
- Qty
- 1~5000
- Unit Price
- Negotiable
- Processing time
- 15 Days
SeekIC Buyer Protection PLUS - newly updated for 2013!
- Escrow Protection.
- Guaranteed refunds.
- Secure payments.
- Learn more >>
Month Sales
268 Transactions
Payment Methods
All payment methods are secure and covered by SeekIC Buyer Protection PLUS.

 MM74C164 Data Sheet
MM74C164 Data Sheet