Features: Pin-equivalent to the general-trade 26LS31 devic with improved speed, reduced power consumptio and significantly lower levels of EMI Four line drivers per package Meets ESDI standards 2.0 ns maximum propagation delay Single 5.0 V ± 10% supply Operating temperature range: -40 °C to +125 °C (wider than the 41 Series) 400 Mbits/s maximum data rate Logic to convert TTL input logic levels to differen tial, pseudo-ECL output logic levels No line loading when VCC = 0 (BDG1A, BDP1A only) High output driver for 50 ? loads <0.2 ns output skew (typical) On-chip 220 ? loads available Third-state outputs available Surge-protection to ±60 V for 10 ms available (BPNGA, BPNPA, BPPGA) Available in four package types ESD performance better than the 41 Series Lower power requirement than the 41 seriesPinout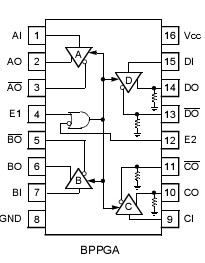 SpecificationsStresses in excess of the absolute maximum ratings can cause permanent damage to the device. These are absolute stress ratings only. Functional operation of the device is not implied at these or any other conditions in excess of those given in the operational sections of the data sheet. Exposure to absolute maximum ratings for extended periods can adversely affect device reliability.
SpecificationsStresses in excess of the absolute maximum ratings can cause permanent damage to the device. These are absolute stress ratings only. Functional operation of the device is not implied at these or any other conditions in excess of those given in the operational sections of the data sheet. Exposure to absolute maximum ratings for extended periods can adversely affect device reliability.
| Parameter |
Symbol |
Min |
Max |
Unit |
| Power Supply Voltage |
VCC |
- |
6.5 |
V |
| Ambient Operating Temperature |
TA |
-40 |
125 |
°C |
| Storage Temperature |
Tstg |
-55 |
150 |
°C |
DescriptionThese quad differential drivers are TTL input-to-pseudo-ECL-differential-output used for digital data transmission over balanced transmission lines. All devices of BPPGA in this family have four drivers with a single enable control in a common package. These drivers of BPPGA are compatible with many receivers, including the Lucent Technologies Microelectronics Group 41 Series receivers and transceivers. BPPGA are pin equivalent to the general-trade 26LS31, but offer increased speed, decreased power consumption, and significantly lower levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI). They replace the Lucent 41 Series drivers.
The BDG1A device is the generic driver in this family and requires the user to supply external resistors on the circuit board for impedance matching.
The BDGLA is a low-power version of the BDG1A, reducing the power requirement by more than one half. The BDGLA features a 3-state output with a typical third-state level of 0.2 V.
The BDP1A is equivalent to the BDG1A but has 220 ? termination resistors to ground on each driver output. This eliminates the need for external pulldown resistors when driving a 100 ? impedance line.
The BPNGA and BPNPA are equivalent to the BDG1A and BDP1A, respectively, except that a lightning protection circuit has been added to the driver
outputs. This circuit will absorb large transitions on the transmission lines without destroying the device.
The BPPGA combines the features of the BPNGA and BPNPA. Two of the gates have their outputs terminated to round through 220 ? resistors while the two remaining gates require external termination resistors.
When the BDG1A and the BDP1A devices are powered down, the output circuit appears as an open circuit relative to the power supplies; hence, they will not load the transmission line. For those circuits with termination resistors, the line will remain impedance matched when the circuit is powered down. The BPNGA, BPNPA, BPPGA, and BDGLA will load the transmission line, because of the protection circuit, when the circuit is powered down.
The packaging options of BPPGA that are available for these quad differential line drivers include a 16-pin DIP; a 16-pin, J-lead SOJ; a 16-pin, gull-wing SOIC; and a 16-pin, narrow-body, gull-wing SOIC.

 BPPGA Data Sheet
BPPGA Data Sheet






