LED and Light Circuit
OPTICALLY_ISOLATED_PRECISION_RECTIFIER
Published:2009/7/20 3:24:00 Author:Jessie | From:SeekIC
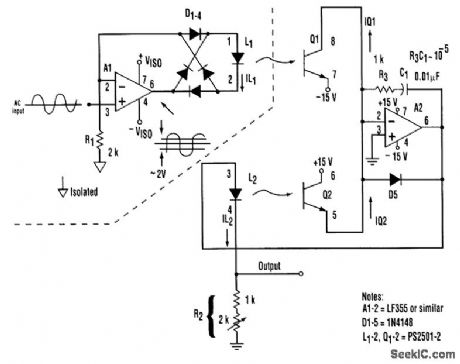

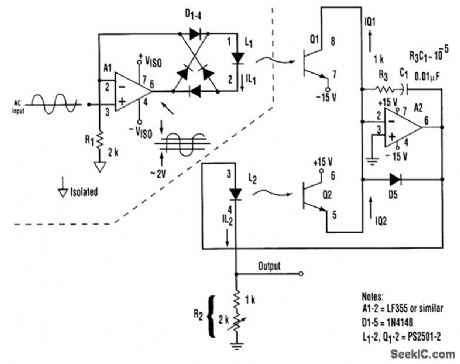
An isolation amplifier and precision rectifier can be combined in one topology, as demonstrated here. It achieves excellent rectification symmetry, zero stability, and good linearity (better than 1 per-cent) and frequency response (>>10kHz), with a minimum of precision components. A1 acts as a volt-age-to-current converter by serving the current through the D1 to D4 bridge and L1. Therefore, the voltage developed across R1 equals the instantaneous input voltage. The diode bridge's full-wave rectification causes L1 to be forward-biased, regardless of the polarity of the input voltage. The magnitude of the bias controls the intensity of optical coupling between L1 and Q1, and, thereby, the magnitude of Q1's collector current. A2 servos the current through L2 and R2 so that the current passed by Q2 balances that passed by Q1. Because of the good tracking of elements of the PS2501-2 dual optoisolator, a constant ratio exists between the L1 and L2 currents. Consequently, R2 can be adjusted so that the out-put voltage across R2 is equal to the rectifier's isolated input voltage. R3 and C1 provide frequency com, pensation for the L2-Q2 feedback loop. D5 prevents potentially destructive reverse bias of L2.
Reprinted Url Of This Article:
http://www.seekic.com/circuit_diagram/LED_and_Light_Circuit/OPTICALLY_ISOLATED_PRECISION_RECTIFIER.html
Print this Page | Comments | Reading(3)

Article Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit
Code: