Control Circuit
Shunt-mode Solar/Wind Charge Controller
Published:2013/3/6 3:10:00 Author:Ecco | Keyword: Shunt-mode , Solar, Wind , Charge Controller | From:SeekIC
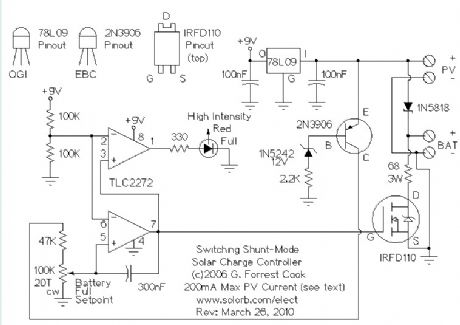
When connecting a solar panel to a rechargeable battery, it is important to use a charge controller circuit to prevent the battery from overcharging. Charge control can be performed with a number of different circuit types. Low-power solar systems can use a series analog charge controller (voltage regulator), an example is shown as the upper part of this circuit. Higher power systems can use a series switching charge controller, such as my SCC3 design. Very large systems, such as grid-tied installations, often use a maximum power-point (MPPT) charge controller. This shunt-mode circuit is best suited for low-power systems, it is more efficient than charge controllers based on series-mode voltage regulators.
Series regulators (both analog and switching) control battery charging by interrupting the flow of current from the solar panel to the battery when the battery reaches a preset full voltage. MPPT controllers use controllable switching regulator circuits to convert PV power to high voltage and back down to lower voltages, they are complicated and require a bit of power to operate, but offer excellent efficiency on high power systems.
This circuit is for a switching shunt-mode charge controller. In a shunt-mode circuit, the solar panel is connected directly to the battery via a series diode. The diode prevents battery current from flowing back through the PV panel at night. When the solar panel charges the battery up to the desired full voltage, the shunt circuit connects a resistive load across the battery in order to absorb the excess PV charging current. An alternate but similar approach to this switching shunt-mode PV regulator is the Analog Shunt-Mode circuit.
Reprinted Url Of This Article:
http://www.seekic.com/circuit_diagram/Control_Circuit/Shunt_mode_Solar_Wind_Charge_Controller.html
Print this Page | Comments | Reading(3)

Article Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit
Code: