Control Circuit
PHASE_CONTROL_1
Published:2009/7/7 9:53:00 Author:May | From:SeekIC
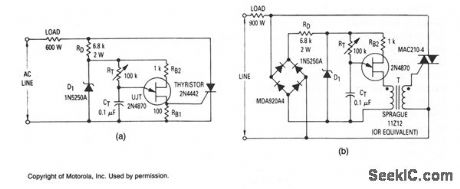
The most elementary application is a half-wave control circuit. The thyristor is acting both as a power control device and as a rectifier, providing variable power to the load during the positive half cycle and no power to the load during the negative half cycle. The circuit is designed to be a two terminal control which can be inserted in place of a switch. If full-wave power is desired as the upper extreme of this control, a switch can be added which will short circuit the SCR when RT is turned to its maximum power position. Full-wave control might be realized by the addition of a bridge rectifter, a pulse transformer, and by chang-ing the thyristor from an SCR to a TRIAC, shown in Fig 50-9b. In this circuit,RB1 is not necessary since the pulse transformer isolates the thyristor gate from the steady-state UJT current. Occasionally, a circuit is required to provide constant output voltage regardless of line voltage changes. Adding potentiorneter P1 to the circuits will provide an approximate solution to this problem. The potentiometer is adjusted to provide reasonably constant output over the desired range of line voltage.
Reprinted Url Of This Article:
http://www.seekic.com/circuit_diagram/Control_Circuit/PHASE_CONTROL_1.html
Print this Page | Comments | Reading(3)

Article Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit
Code: