Control Circuit
Engine Running Detector, Load Switch
Published:2013/10/29 20:40:00 Author:lynne | Keyword: Engine Running Detector, Load Switch | From:SeekIC
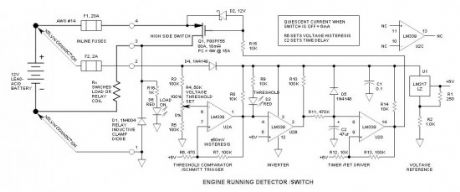
This circuit determines when an engine is running, and when running, it turns on a solid-state switch to automatically power accessories. It does this simply by measuring battery voltage—when not charging, battery voltage is less than approx. 13.2V—when charging, it is greater than approx. 14.0V. Seems like a simple task, does it not? If so, why are there not already devices available to do this seemingly simple task?
While the concept is simple, there are numerous problems involved as follows:
Voltage must be sensed as close to the battery as possible, and voltage sense wiring must be separate from power wiring—hence the requirement for the Kelvin connection. This is why I wrote the recent article:What is a Kelvin Connection?
Since this circuit is connected directly to the battery, circuit protection is absolutely essential. This is why I wrote the recent article:Low Voltage & Automotive Circuit Protection.
Voltage threshold must be accurate—requires stable voltage reference.
Circuit must have hysteresis for positive switching.
Load switch must have substantial delay to prevent unintended or nuisance switching.
Quiescent current must be low to prevent battery discharge.
Charging system must function correctly—alternator must float charge the battery as well as power all connected accessories when engine is at idle speed.
Due to variations in battery charging voltage in different systems and a relatively narrow voltage threshold window, there is no one size fits all voltage setting. As a result, the threshold must be adjustable.
Due to these complexities, this circuit is not recommended for the novice. However, if installed using proper circuit protection & wiring practices, the only failure mode is unintended battery discharge should it not automatically disconnect the load.
Reprinted Url Of This Article:
http://www.seekic.com/circuit_diagram/Control_Circuit/Engine_Running_Detector_Load_Switch.html
Print this Page | Comments | Reading(3)

Article Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit
Code: