Basic Circuit
POWER_CONSUMPTION_LIMITER
Published:2009/7/10 2:04:00 Author:May | From:SeekIC
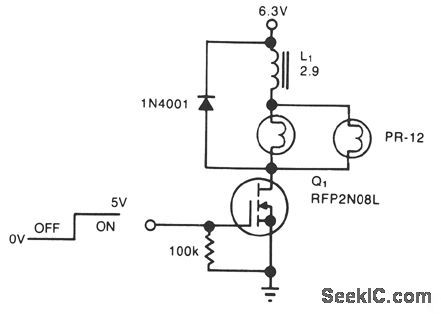

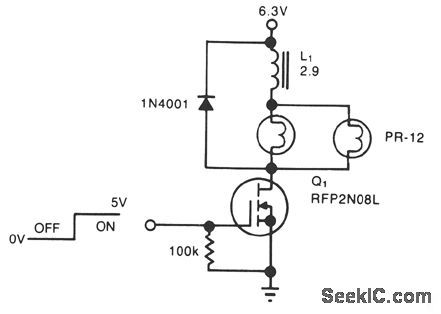
A simple solenoid driver uses incandescent lamp filaments as on-indicators to limit power con-sumption. High magnetic reluctance (opposition to flux) in the coil of an armature-driven device, such as a solenoid or relay, calls for a surge of activation current, followed by a lower dc level to remain on,since surge to on-current ratio is typically 5:1. The cold filament allows a surge of coil-activation current to pass through; as the filament heats up, it throttles the current to a more reasonable hold value. The solenoid driver circuit offers these features: ●5-V logic swings turn the power-MOSFET switch, Q1, fully on and off. ●Two low-cost flashlight lamps, in parallel, handle the peak current. Because their dc current is only 50% of peak and because they operate at 60% of their rated voltage, the lamps have an operating life of 12,000 hours. Further, the lamp filaments' positive temperature coefficients raise each filament's resistance. This rise in resistance liminates current-hogging problems and provides short-circuit protection.●The steady-state on-current is 700 mA, vs. 1700 mA without the lamps.
●A 4.6-V min supply rating allows battery opera-tion.
Reprinted Url Of This Article:
http://www.seekic.com/circuit_diagram/Basic_Circuit/POWER_CONSUMPTION_LIMITER.html
Print this Page | Comments | Reading(3)

Article Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit
Code: