Basic Circuit
BF_MODULATOR
Published:2009/7/8 4:36:00 Author:May | From:SeekIC
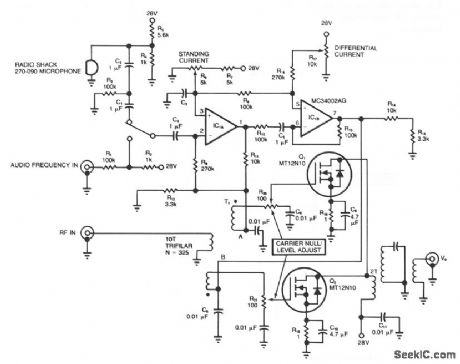
Because power MOSFETs offer high power gain at both audio and radio frequencies, they are useful in many areas of radio-circuit design. For rf applications, a MOSFET's large safe operating area, VDS vs ID, protects it against damage from reflected rf energy. As a modulator, a MOSFET's transfer linearity aids fidelity. In the suppressed-carrier modulator, an rf signal is applied to the primary of transformer T1, whose secondaries provide equal-amplitude, opposite-phase rf drive signals to output FETs Q1 and Q2.Output V0 is zero when no audio-frequency signals are present, because the opposite-phase rf signals from Q1 and Q2 cancel. When audio-frequency signals appear at nodes A and B, you obtain a modulated rf output (V0). Source resistors R18 and R19 improve the dc stability and low-frequency gain. A phase inverter, based on the dual op amp IC1A and IC1B, generates the out-of-phase, equal-amplitude, audio-frequency modulation signals.
Reprinted Url Of This Article:
http://www.seekic.com/circuit_diagram/Basic_Circuit/BF_MODULATOR.html
Print this Page | Comments | Reading(3)

Article Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit
Code: