555 Circuit
Work Principle of 555 Monostable Model
Published:2011/7/5 0:01:00 Author:Zoey | Keyword: Work Principle, 555 Monostable Model | From:SeekIC
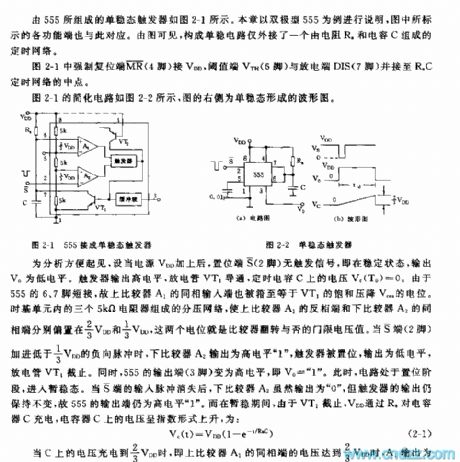

The Monostable multi-vibrator composed of 555 has been shown in the picture 2-1.This chapter takes the bipolar 555 as an example; functional terminals marked in the picture are relevant to each other. This monostable circuit has jointed a time network that consists of a resistance Ra and a capacitor C.
In the picture 2-1, the coercive resetion terminal pin 4 connects VDD, threshold terminal pin 6 VTH and discharge terminal DIS pin7 connect to the midpoint of RaC time network. Picture 2-2 is the simplified circuit, the right one is the waveform of monostable circuit.
When in a stable state, the output voltage V0 is in low level; when the circuit in a temporary stable state, voltage on the capacitor ascends exponentially:
Vc(t)=VDD(1-e-1/RaC)
When voltage on the capacitor reaches to 2/3VDD, the circuit backs to be stable. When the circuit is in a temporary stable state, the time that V0(t) takes to ascend from 0 to 2/3VDD is td:
2/3VDD-VDD(1-e-td/RaC)
From the formulas above, we can conclude that time of outputting high level:
td=-RaCln(1/3)
td≈1.1RaC(s)
The prolonged time of monostable model td is irrelevant to outer voltage VDD but is determined by time constant of time network.
Reprinted Url Of This Article:
http://www.seekic.com/circuit_diagram/555_Circuit/Work_Principle_of_555_Monostable_Model.html
Print this Page | Comments | Reading(3)

Article Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit
Code: